GMPC II communication driver is the driver to communicate with power meter GIMAC/GIMACII/GIMACIII/GIMAC II Plus model of LSIS Co., Ltd. in Korea.
GIMAC II Plus model communicate with GMPC controller( GMPC I, GMPC II, GMPC III, GMPC V, ... ) and computer read and write GMPC's data.
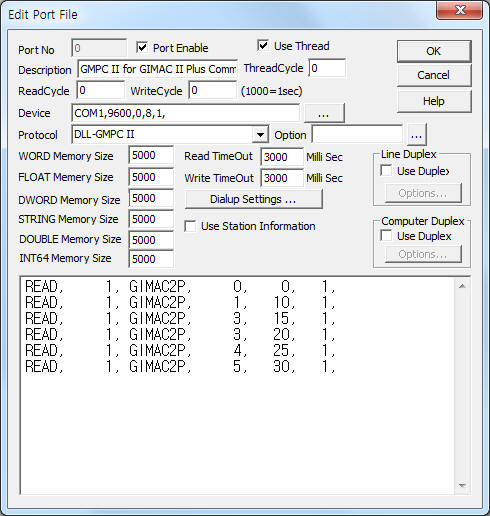
<Figure 1> is read setting example of GMPC II communication driver for GIMAC II Plus model.
 |
| <Figure 1> Read setting example of GMPC II communication driver for GIMAC II Plus model |
Device part of <Figure 1> input Com Port(COM1 or TCP/IP, UDP/IP, etc), Baud Rate(9600), Parity Bit(0), Data Bit(8), Stop Bit(1) respectively according to setting of GMPC.
Baud rate, parity bit, data bit, stop bit can set by using switch of rear or front panel(GMPC controller).
GMPC II communication driver read schedule for GIMAC II Plus
Read schedule setting parameters are as follows:
1) STATION – GIMAC II Plus controller station number = 0 ~ 255.
2) Controller Model – Model = GIMAC2P(when using GIMAC II Plus model).
3) Read data type – Data type = 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6.... ( Cmd - 10h, refer to reference manual of GIMAC II Plus )
4) Save Start Address for Communication Server – saveing start address of Communication Server.
5) Read Size – Read size. Fixed according to read data type. ( Refer to <Table 1>, <Table 2> )
6) Sub1 command - Input Sub1 command according to controller model.
7) Sub2 command - Input Sub 2 command according to controller model.
Read schedule example)
READ, 1, GIMAC2P, 0, 0, 1,
READ, 1, GIMAC2P, 1, 10, 1,
READ, 1, GIMAC2P, 3, 15, 1,
READ, 1, GIMAC2P, 3, 20, 1,
READ, 1, GIMAC2P, 4, 25, 1,
READ, 1, GIMAC2P, 5, 30, 1,
<Table 1> is data saving address and contents for each read command.
<Table 2> is each bit value for I/O status read command.
Note) Data type = Cmd number - 10h. Please refer to GIMAC II Plus reference manual for more information about Cmd, Sub1, Sub2, etc.
| Data type | Extra2 | Extra3 | Contents | Data size or unit | Data Saving Address |
| 0 | - | Read of I/O status | 6 BYTE ( Bit ) | Refer to <Table 2> |
|
| 1 | Read of R, S, T phase current | 3 Float data | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : Ir, Is, It |
||
| 2 | Read of Vab, Vbc, Vca voltage | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : Vab, Vbc, Vca |
|||
| 3 | Power factor,active/reactive power | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : power factor,active/reactive power |
|||
| 4 | Frequency, amount of total active/reactive power | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : frequency, amount of total active/reactive power |
|||
| 5 | Read of Va, Vb, Vc phase voltage | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : Vr, Vs, Vt |
|||
| 6 | 0 | 0 | Total apparent power, reverse active power quantity, zero-phase sequence voltage |
3 Float data | Start Add + 0 : total Total apparent power, Start Add + 1 : reverse active power quantity, Start Add + 2 : zero-phase sequence voltage |
| 1 | 0 | positive phase sequence voltage, negative phase sequence voltage, voltage unblanced factor |
Start Add + 0 : positive phase sequence voltage, Start Add + 1 : negative phase sequence voltage, Start Add + 2 : voltage unblanced factor |
||
| 2 | 0 | positive phase sequence current, negative phase sequence current, current unblanced facto |
Start Add + 0 : positive phase sequence current, Start Add + 1 : negative phase sequence current, Start Add + 2 : current unblanced factor |
||
| 3 | 0 | Vo max, Vo max time | 1 Float data, 6 Byte data |
Start Add + 0 : Vo max Start Add + 1 ~ 6 : Vo max time year, month, day, hour, minute, second |
|
| 7 | 0 | 0 | A, B, C phase voltage | 3 Float data | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : A, B, C phase voltage |
| 1 | 0 | AB, BC, CA phase voltage | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : AB, BC, CA phase voltage |
||
| 2 | 0 | A, B, C phase current | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : A, B, C phase current |
||
| 8 | 0 | 0 | A, B, C phase active power | 3 Float data | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : A, B, C phase active power |
| 1 | 0 | A, B, C phase reactive power | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : A, B, C phase reactive power |
||
| 2 | 0 | A, B, C phase apparent power | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : A, B, C phase apparent power |
||
| 3 | 0 | A, B, C phase amount of active power | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : A, B, C phase amount of active power |
||
| 4 | 0 | A, B, C phase amount of reactive power | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : A, B, C phase amount of reactive power |
||
| 9 | 0 | 0 ~ 4 | 3 harmonic data of A phase voltage( 1 ~ 15 harmonic) | 3 Float data | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : 3 harmonic data of A phase voltage |
| 9 | 1 | 0 ~ 4 | 3 harmonic data of B phase voltage( 1 ~ 15 harmonic) | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : 3 harmonic data of B phase voltage |
|
| 2 | 0 ~ 4 | 3 harmonic data of C phase voltage( 1 ~ 15 harmonic) | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : 3 harmonic data of C phase voltage |
||
| 3 | 0 ~ 4 | 3 harmonic data of A phase current( 1 ~ 15 harmonic) | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : 3 harmonic data of A phase current |
||
| 4 | 0 ~ 4 | 3 harmonic data of B phase current( 1 ~ 15 harmonic) | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : 3 harmonic data of B phase current |
||
| 5 | 0 ~ 4 | 3 harmonic data of C phase current( 1 ~ 15 harmonic) | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : 3 harmonic data of C phase current |
||
| 6 | 0 | A, B, C phase voltage THD | 3 Float data | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : A, B, C phase voltage THD |
|
| 7 | 0 | A, B, C phase current THD | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : A, B, C phase current THD |
||
| 8 | 0 | AB, BC, CA phase voltage THD | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : AB, BC, CA phase voltage THD |
||
| 10(0Ah) | 1 | 0 | A[0], A[1] current | 2 Float data | Start Add + 0 ~ 1 : A[0], A[1] current |
| 2 | 0 | Demand la, la time | 1 Float data. 6 Byte data |
Start Add + 0 : Demand la Start Add + 1 ~ 6 : Demand la time year, month, day, hour, minute, second |
|
| 2 | 1 | Demand lb, lb time | Start Add + 0 : Demand lb Start Add + 1 ~ 6 : Demand lb time year, month, day, hour, minute, second |
||
| 2 | 2 | Demand lc, lc time | Start Add + 0 : Demand lc Start Add + 1 ~ 6 : Demand lc 시간 년,월,일,시,분,초 |
||
| 3 | 0 | Max Demand W, time | Start Add + 0 : Max Demand W Start Add + 1 ~ 6 : Demand W time year, month, day, hour, minute, second |
||
| 3 | 1 | Max W, Max W time | Start Add + 0 : Max W Start Add + 1 ~ 6 : Max W time year, month, day, hour, minute, second |
||
| 4 | 0 | A, B, C phase current TDD | 3 Float data | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : A, B, C phase current TDD |
|
| 5 | 0 | A, B, C phase current Kfactor | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : A, B, C phase current Kfactor |
||
| 6 | 1 ~ 3 | A~C phase current Max, Min, Average | 3 Float data | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : A~C phase current Max, Min, Average |
|
| 6 | 4 ~ 6 | A~C phase voltage Max, Min, Average | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : A~C phase voltage Max, Min, Average |
||
| 6 | 7 ~ 9 | AB~CA phase voltage Max, Min, Average | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : AB~CA phase voltage Max, Min, Average |
||
| 6 | A | Total power factor Max, Min, Average | 3 Float data | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : total power factor Max, Min, Average |
|
| 6 | B | Total power Max, Min, Average | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : Total power Max, Min, Average |
||
| 6 | C | Total reactive power Max, Min, Average | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : Total reactive power Max, Min, Average |
||
| 6 | D | Total apparent power Max, Min, Average | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : Total apparent power Max, Min, Average |
||
| 6 | E | Frequency Max, Min, Average | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : frequency Max, Min, Average |
||
| 6 | F | Positive phase sequence voltage Max, Min, Average | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : positive phase sequence voltage Max, Min, Average |
||
| 6 | 10 | Negative phase sequence voltage Max, Min, Average | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : negative phase sequence voltage Max, Min, Average |
||
| 6 | 11 | Voltage unblanced factor Max, Min, Average | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : voltage unblanced factor Max, Min, Average |
||
| 6 | 12 | Positive phase sequence current Max, Min, Average | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : positive phase sequence current Max, Min, Average |
||
| 6 | 13 | Negative phase sequence current Max, Min, Average | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : negative phase sequence current Max, Min, Average |
||
| 6 | 14 | Current unblanced factor Max, Min, Average | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : current unblanced factor Max, Min, Average |
||
| 6 | 15 ~ 17 | A, B, C phase power factor Max, Min, Average | 3 Float data | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : A, B, C phase power factor Max, Min, Average |
|
| 6 | 18 ~ 1A | A, B, C phase active power Max, Min, Average | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : A, B, C phase active power Max, Min, Average |
||
| 6 | 1B ~ 1D | A, B, C phase reactive power Max, Min, Average | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : A, B, C phase reactive power Max, Min, Average |
||
| 6 | 1E ~ 20 | A, B, C phase apparent power Max, Min, Average | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : A, B, C phase apparent power Max, Min, Average |
||
| 6 | 21 ~ 23 | A~C phase voltage THD Max, Min, Average | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : A~C phase voltage THD Max, Min, Average |
||
| 6 | 24 ~ 26 | A~C phase current THD Max, Min, Average | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : A~C phase current THD Max, Min, Average |
||
| 6 | 27 ~ 29 | A~C phase current TDD Max, Min, Average | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : A~C phase current TDD Max, Min, Average |
||
| 6 | 2A ~ 2C | A~C phase current K factor Max, Min, Average | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : A~C phase current K factor Max, Min, Average |
||
| 11(0Bh) | 0 | 0 | Operating time, CB ON time | 2 Dword data | Start Add + 0 ~ 1 : operating time, CB ON time |
| 1 | 0 | Number of CB ON, number of DO01 ~ 02 ON | 3 Dword data | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : number of CB ON, number of DO01 ~ 02 ON |
|
| 1 | 1 | Number of DO03 ~ 05 ON | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : number of DO03 ~ 05 ON |
||
| 1 | 2 | Number of DO06 ~ 08 ON | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : number of DO06 ~ 08 ON |
||
| 2 | 0 | Logging start time | 6 Byte data | Start Add + 0 ~ 5 : start time hour, month, day, hour, minute, second |
|
| 2 | 1 | A, B, C phase current Max, Min, Average occur time | 3 Dword data | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : A, B, C phase current Max, Min, Average occur time |
|
| 2 | 2 | A, B, C phase voltage Max, Min, Average occur time | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : A, B, C phase voltage Max, Min, Average occur time |
||
| 2 | 3 | AB, BC, CA phase voltage Max, Min, Average occur time | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : AB, BC, CA phase voltage Max, Min, Average occur time |
||
| 2 | 4 | Total power factor, total power, Total reactive power Max, Min, Average occur time | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : total power factor, total power, Total reactive power Max, Min, Average occur time |
||
| 2 | 5 | Total apparent power, frequency Max, Min, Average occur time | 2 Dword data | Start Add + 0 ~ 1 : total apparent power, frequency Max, Min, Average occur time |
|
| 2 | 6 | Positive/negative phase sequence voltage unblanced factor Max, Min, Average occur time | 3 Dword data | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : positive/negative phase sequence voltage unblanced factor Max, Min, Average occur time |
|
| 2 | 7 | Positive/negative phase sequence current unblanced factor Max, Min, Average occur time | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : Positive/negative phase sequence current unblanced factor Max, Min, Average occur time |
||
| 2 | 8 | A, B, C phase power factor Max, Min, Average occur time | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : A, B, C phase power factor Max, Min, Average occur time |
||
| 2 | 9 | A, B, C phase active power Max, Min, Average occur time | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : A, B, C phase active power Max, Min, Average occur time |
||
| 2 | A | A, B, C phase reactive power Max, Min, Average occur time | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : A, B, C phase reactive power Max, Min, Average occur time |
||
| 2 | B | A, B, C phase apparent power Max, Min, Average occur time | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : A, B, C phase apparent power Max, Min, Average occur time |
||
| 2 | C | A, B, C phase voltage THD Max, Min, Average occur time | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : A, B, C phase voltage THD Max, Min, Average occur time |
||
| 2 | D | A, B, C phase current THD Max, Min, Average occur time | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : A, B, C phase current THD Max, Min, Average occur time |
||
| 2 | E | A, B, C phase current TDD Max, Min, Average occur time | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : A, B, C phase current TDD Max, Min, Average occur time |
||
| 2 | F | A, B, C phase current Kfactor Max, Min, Average occur time | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : A, B, C phase current Kfactor Max, Min, Average occur time |
||
| 13(0Dh) | 0 | 0 | Wiring type, frequency, CT ratio | 2 Byte data, 1 Word data |
Start Add + 0 : wiring type ( 1 = 3 phase 4 line, 2 = 3 phase 3 line Y, 3 = 3 phase 3 line delta, 4 = 1 phase 3 line, 5 = 1 phase 2 line ) Start Add + 1 : frequency (50 or 60) Start Add + 2 : CT ratio |
| 1 | 0 | PT, GPT setting value | 2 Float data | Start Add + 0 ~ 1 : PT, GPT setting value |
|
| 4 | 0 | Demand Time | 1 Word data | Start Add + 0 : Demand Time |
|
| 5 | 0 | DI 1 ~ 6 set status | 6 Word data | Start Add + 0 ~ 5 : DI 1 ~ 6 set status |
|
| 5 | 1 | DI 7 ~ 8 set status | 2 Word data | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : DI 7 ~ 8 set status |
|
| 6 | 0 | DO 1 ~ 6 set status | 6 Word data | Start Add + 0 ~ 5 : DO 1 ~ 6 set status |
|
| 6 | 1 | DO 7 ~ 8 set status | 2 Word data | Start Add + 0 ~ 2 : DO 7 ~ 8 set status |
|
| <Table 1> Data saving address and contents for each read command | |||||
Data Saving Address |
Status value for each bit |
Remarks |
Start Add + 0 |
0 ~ 7 bit = DI 01 ~ 08 status |
status value for DI |
Start Add + 1 |
0 ~ 7 bit = Latch DI 01 ~ 08 status |
|
Start Add + 2 |
0 ~ 7 bit = DO 01 ~ 08 status |
|
Start Add + 3 |
0 ~ 3 bit = - , 4 bit = CB Off DO, 5 bit = CB On DO, 6 bit = CB Off DI, 7 bit = CB On DI |
|
Start Add + 4 |
0 bit = Sys. Error, 1 bit = Alarm, 2 bit = EVENT, 3 bit = - , 4 bit = Remote/Local, 5 ~ 7 bit = - |
|
Start Add + 5 |
always 0x91 |
Device ID |
| <Table 2> Each bit value for I/O status read command | ||
GMPC II communication driver store the same data in WORD, DWORD, FLOAT memory, but the data format are different.
If you click the icon ![]() in protocol option part, you
can see the dialogue box such as <Figure 2>. you can also set read schedule by
using this part.
in protocol option part, you
can see the dialogue box such as <Figure 2>. you can also set read schedule by
using this part.
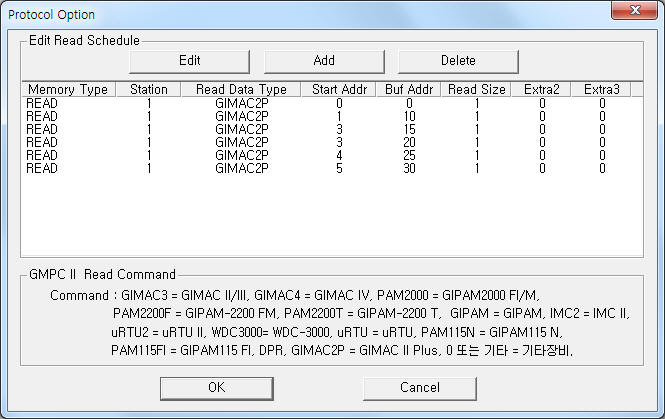 |
| <Figure 2> Example of GMPC II communication driver’s Option dialogue box |
You can set read schedule by using ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() button and listbox of <Figure
2>.
button and listbox of <Figure
2>.
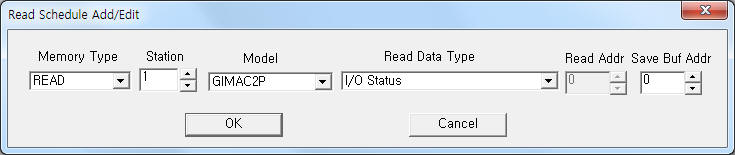 |
| <Figure 3> Example of GMPC II communication driver’s read schedule Add/Edit dialogue box |
When you click Add button or Edit button in dialogue box of <Figure 2>, dialogue box of <Figure 3> is shown.
You can write GIMAC II Plus equipment's setting value by using write settings.
Digital Write
Digital write setting parameters are as follows:
1) PORT Port no. (0 ~ 255)
2) STATION GIMAC II Plus controller station number = 0 ~ 255.
3) ADDRESS Setting data type(hex-decimal unit) number of Sub2, refer to <Table 3>.
4) Extra1 Model name = GIMAC2P. ( GIMAC II Plus model )
5) Extra2 Load control, Reset or Clear setting.
0 – Load control,
1 – Reset or Clear command.
Command |
Address(Sub2) number |
Contents |
Load control |
01h |
CB ON control |
02h |
CB OFF control |
|
10h |
DO 1 ON control |
|
11h |
DO 2 ON control |
|
12h |
DO 3 ON control |
|
13h |
DO 4 ON control |
|
14h |
DO 5 ON control |
|
15h |
DO 6 ON control |
|
16h |
DO 7 ON control |
|
17h |
DO 8 ON control |
|
18h |
DO 1 OFF control |
|
19h |
DO 2 OFF control |
|
1Ah |
DO 3 OFF control |
|
1Bh |
DO 4 OFF control |
|
1Ch |
DO 5 OFF control |
|
1Dh |
DO 6 OFF control |
|
1E6h |
DO 7 OFF control |
|
1Fh |
DO 8 OFF control |
|
Reset or Clear command |
00h |
Vo MAX reset |
01h |
DEMAND CURRENT reset |
|
02h |
MAX DEMAND W reset |
|
03h |
MAX W reset |
|
04h |
WH reset |
|
05h |
VARH reset |
|
06h |
rWH reset |
|
07h |
EVENT clear |
|
08h |
RUN TIME clear |
|
09h |
|
|
0Ah |
CB ON COUNT clear |
|
0Bh |
DO 1 ON COUNT clear |
|
0Ch |
DO 2 ON COUNT clear |
|
0Dh |
DO 3 ON COUNT clear |
|
0Eh |
DO 4 ON COUNT clear |
|
0Fh |
DO 5 ON COUNT clear |
|
10h |
DO 6 ON COUNT clear |
|
11h |
DO 7 ON COUNT clear |
|
12h |
DO 8 ON COUNT clear |
|
15h |
FAULT RESET |
|
| <Table 3> Setting element and data range for Digital write | ||
Note) Digital write for GIMAC II Plus can control when the equipment's setting is 'remote'.
Write example 1)
PORT : 0 Station : 1, ADDRESS : 0001, EXTRA1 : GIMAC2P, EXTRA2 : 0
The setting parameter shown above is CB ON control example for 1 controller station GIMAC II Plus.
CB ON write command can control when the controller's setting is 'remote'.
Write example 2)
PORT : 0 Station : 1, ADDRESS : 0002, EXTRA1 : GIMAC2P, EXTRA2 : 0
The setting parameter shown above is CB OFF control example for 1 controller station GIMAC II Plus.
CB OFF write command can control when the controller's setting is 'remote'.
Write example 3)
PORT : 0 Station : 1, ADDRESS : 0010, EXTRA1 : GIMAC2P, EXTRA2 : 0
The setting parameter shown above is DO 1 On control example for 1 controller station GIMAC II Plus.
DO 1 On write command can control when the controller's setting is 'remote' and current status is 'Off'.
Write example 4)
PORT : 0 Station : 1, ADDRESS : 0018, EXTRA1 : GIMAC2P, EXTRA2 : 0
The setting parameter shown above is DO 1 Off control example for 1 controller station GIMAC II Plus.
DO 1 Off write command can control when the controller's setting is 'remote' and current status is 'On'.
Write example 5)
PORT : 0 Station : 1, ADDRESS : 0000, EXTRA1 : GIMAC2P, EXTRA2 : 1
The setting parameter shown above is reset of Vo MAX value example for 1 controller station GIMAC II Plus.
Vo MAX value reset command can control when the controller's setting is 'remote'.
Write example 6)
PORT : 0 Station : 1, ADDRESS : 0010, EXTRA1 : GIMAC2P, EXTRA2 : 1
The setting parameter shown above is a example of clear DO 6 On count.
Clear DO 6 On count command can control when the controller's setting is 'remote'.
Analog Write
GMPC II communication driver for GIMAC II Plus model don't support analog write.
Connection of main power and communication cable are as follows.
Connection of main power
Please connect 100 ~ 230V AC main power to P( + ), N( - ) connector at GIMAC II Plus controller's rear panel such as <Figure 4>.
<Figure 5> is appearance of GIMAC II Plus controller.
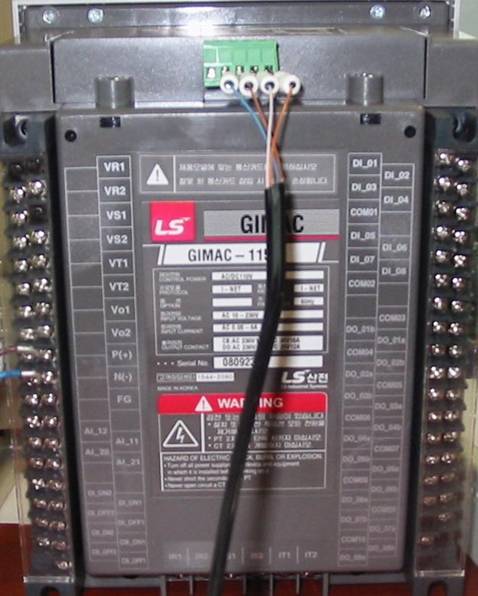 |
| <Figure 4> Connection example of main power and communication cable to GIMAC II Plus controller |
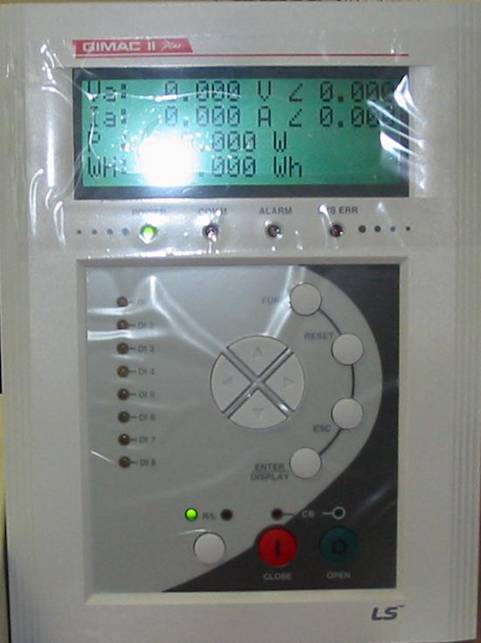 |
| <Figure 5> Appearance of GIMAC II Plus controller |
Connection of I-NET communication cable
Please connect I-NET RS-485 communication cable to Rx0, Rx1, Tx0 , Tx1 connector such as <Figure 4>.
Setting of protocol
GIMAC II Plus controller can use GIMAC II protocol or GIMAC II Plus protocol.
Protocol setting method is as follows.
1) Press 'FUNC' button. Then will be displayed 'password input' menu.
2) Input password(default = 0000) by using 'UP', 'DOWN' button and press 'ENTER'button. Then will be displayed 'main setting' menu.
3) Select ‘1. DEVICE CONFIG’ menu and press 'ENTER' button 2 times and select ‘2. COMM. SET’ menu.
4) Please select 'I-NET' menu by pressing 'RIGHT' button 3 times.
5) Select G2(GIMAC II protocol), G2+(GIMAC II Plus protocol) protocol by using 'UP', 'DOWN' button.
6) Input ‘ENTER’ button and reset the GIMAC II Plus controller.
Note) When you connect GIMAC-IV and GMPC, you have to connect Rx = Tx, Tx = Rx respectively. ( I-NET cable = offered by LSIS Co., Ltd. when you buying GMPC or GIMAC II Plus)
Connection of GMPC V almost equal with GMPC III. So you can refer to connection of GMPC III part.
<Figure 6> is apperance of GMPC V controller.
 |
| <Figure 6> Apperance of GMPCV controller |
Note) Password input method : you can input 'password' by using 4 button of frong panel. ( Inital(default) Password : press 'FUNCTION', 'SELECT', 'UP', 'ENTER' button 2 times by turns )
Setting of GMPC V)
1. Time & Date : Date and Time setting of GMPC V.
2. Model : Model, protocol and communication method of GMPC V.
Model | Protocol : select GMP(I-NET protocol of GMPC) or MODBUS protocol,
Model | Media : select communication media of GMPC V.
Model | Main Port : select Primary(P) or Secondary(S).
3. Serial : select Com1 or Com2 port of GMPC V.
4. Network(This) : select LAN1, LAN2 Ethernet port.
Network(This) | Ethernet Port : select primary ethernet port of GMPC V.
Network(This) | IP_0 : input IP Address of Primary Ethernet,
Network(This) | Port_0 No_0 : input Port number of Primary Ethernet,
Network(This) | Netmask_0 : input Subnet mask of Primary Ethernet,
Network(This) | Gateway_0 : input Gateway IP Address of Primary Ethernet,
Network(This) | Host_IP0 : input Host(PC, etc) IP Address of Primary Ethernet.
After setting GMPC V controller, save the setting by using 'ENTER' button.
Also, you have to reset(power off and power on) in order to apply the setting value. (don't reset, GMPC V use the old setting value)
Note) When you using the 'Ethernet' communication, you have to set Host(PC, etc) IP address at GMPC V controller.
Also if you don't use gateway at network, please set 'Gateway' IP address to '0.0.0.0'.
Note) You must input power for the first time of GIMAC II Plus, etc, and input power GMPC V.
If you input power GMPC V the first and input GIMAC II Plus, etc, GMPC V can't find connected equipment. So it may not be able to communicate with connected equipment.