SIEMENS S7-200 PPI is driver to communicate with PLC S7-200 model of SIEMENS Corp., in Germany.
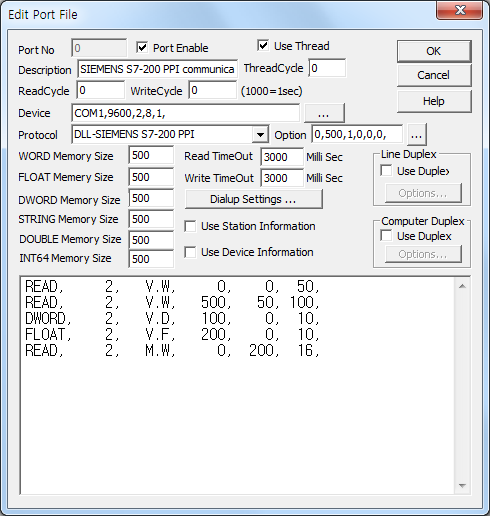
<Figure 1> is read setting example of SIEMENS S7-200 PPI communication driver.
 |
| <Figure 1> Read setting example of SIEMENS S7-200 PPI driver |
Device part of <Figure 1> input Com Port(COM1), Com Baud(9600), Parity Bit(2), Data Bit(8), Stop Bit(1) respectively, according to device.
Also, you can enter the Address of Computer(0 ~ 126, Default = 0), Result of WORD address(0 ~ 9999, Default = 500) which comparing with PLC memory data, Whether to use Read/Write address as BYTE unit ( 0 = Don't care, 1 = Use as BYTE unit, Default = 1 ), Whether to save read data as BYTE unit( 0 = Not use, 1 = Save as BYTE unit, Default = 0 ), Protocol Type(0 = Normal, 1 = New Type, 2 = Extended Code, Default = 0) and Read delay time after writing(0 ~ 1000mSec, Default = 0) at Option part by classifying as comma( , ).
Notice) You can set Com Baud of PPI protocol for S7-200 PLC as 9600, 19200 and etc(by using STEP 7-Micro/Win program), and Parity Bit, Data Bit and Stop Bit are fixed as 2, 8 and 1.
SIEMENS_S7-200 PPI communication driver's read schedule
Read schedule setting parameters are as follows:
1) STATION – PLC address number between 0 and 126.
2) Read Data Type – Input among V.y, M.y, I.y, Q.y, SM.y, S.y, C, T, AI and AQ. ( Refer to <Table 1> )
y = Read data type among Blank, B, W, D and F
( B : BYTE, W or blank, etc : WORD, D : DWORD, F : FLOAT )
3) Read Start Address – Start address to read in designated memory.
In case of using Read/Write address as BYTE unit( set at Option ) – Always BYTE unit address,
In case of not using Read/Write address as BYTE unit( set at Option ) - BYTE/WORD/DWORD/FLOAT unit number,
But, T, C, AI and AQ area always use WORD unit.
4) Save Start Address for Communication Server - Saving start address of Communication Server.
5) Read Size - The number of BYTE/WORD/DWORD/FLOAT to read.
(It is possible to read maximum 222 BYTE/111 WORD/55 DWORD/55 FLOAT. There is difference according to model)
Read schedule example)
| READ | STATION | Read Data Type | Read Start Address | Save Start Address for Communication Server | Read Size |
| READ | 2 | V.W | 0 | 0 | 50 |
| READ | 2 | V.W | 500 | 50 | 100 |
| DWORD | 2 | V.D | 100 | 0 | 10 |
| FLOAT | 2 | V.F | 200 | 0 | 10 |
| READ | 2 | M.W | 0 | 200 | 16 |
Memory Area |
Contents |
Remarks |
V |
Data Block |
|
M |
Memory Area |
|
I |
Input Area |
|
Q |
Output Area |
|
SM |
SM Area |
|
S |
S Area |
|
C |
Count Area |
Word Only Memory |
T |
Timer Area |
|
AI |
AI Memory |
|
AQ |
AO Memory |
|
| <Table 1> Memory area type and contents of Siemens S7-200 PPI communication driver | ||
If you click the icon ![]() in protocol option part of
<Figure 1>, you can see the dialog box such as <Figure 2>. You can also set read
schedule by using this part.
in protocol option part of
<Figure 1>, you can see the dialog box such as <Figure 2>. You can also set read
schedule by using this part.
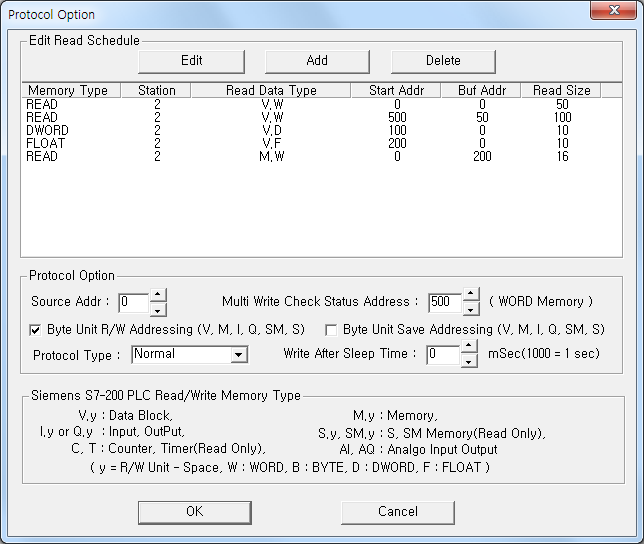 |
| <Figure 2> Example of SIEMENS S7-200 PPI driver's Option dialog box |
You can set read schedule by using ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() button
and listbox of <Figure 3>.
button
and listbox of <Figure 3>.
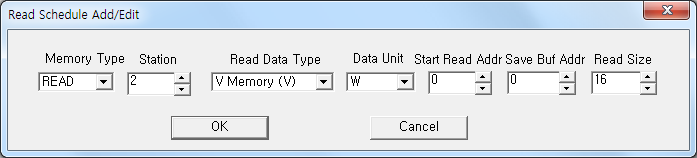 |
| <Figure 3> Example of SIEMENS S7-200 PPI driver's read schedule Add/Edit dialog box |
When you click Add button or Edit button in dialog box of <Figure 2>, dialog box of <Figure 3> is shown.
You can change PLC memory as set value by using writing settings.
Digital Write
Digital write setting parameters are as follows :
1) Port Connected port number. (Not COM number)
2) Station Input PLC address between 0 and 126.
3) Address 0000 ~ xxxF,
High 3 digits are output address of BYTE unit as decimal unit
( But, in case of not using Read/Write address as BYTE unit, it is output address of BYTE/WORD/DWORD/FLOAT unit )
Sub 1 digit is bit position between no.0 and no.F.
4) Extra1 Input among V.y, M.y, I.y and Q.y.
y = Data type to read among Blank, B, W, D and F
( B : BYTE, W or Blank, etc : WORD, D : DWORD, F : FLOAT )
5) Extra2 In case of DWORD/FLOAT output, designate 0 ~ 15 bit and 16 ~ 32 bit
0 : Bit between no.0 and no.15( 00h ~ 0Fh ),
1 : Bit between no.16 and no.31( 10h ~ 1Fh ).
Writing example 1)
Port : 0 Station : 0 Address : 0127, Extra1 : V.B, Extra2 : Blank
If you set as above and write digital value, you can ON/OFF the 8th (no.7) bit value of V memory's no.12 BYTE.
Writing example 2)
Port : 0 Station : 0 Address : 006F, Extra1 : V.W, Extra2 : Blank
If you set as above and write digital value, you can ON/OFF the 16th(no.F) bit value of V memory's no.6 BYTE(but, in case of not using Read/Write address as BYTE unit, it is no.6 WORD).
Writing example 3)
Port : 0 Station : 0 Address : 0160, Extra1 : V.W, Extra2 : Blank
If you set as above and write digital value, you can ON/OFF the first (no.0) bit value of V memory's no.16 BYTE(but, in case of not using Read/Write address as BYTE unit. it is no.16 WORD).
Writing example 4)
Port : 0 Station : 0 Address : 0069, Extra1 : V.D, Extra2 : 0
If you set as above and write digital value, you can ON/OFF the 10th(no.9) bit value of V memory's no.6 WORD(but, in case of not using Read/Write address as BYTE unit, it is no.6 DWORD).
Writing example 5)
Port : 0 Station : 0 Address : 004F, Extra1 : M, Extra2 : Blank
If you set as above and write digital value, you can ON/OFF no.F bit value of M memory's no.4 byte(but, in case of not using Read/Write address as BYTE unit, it is no.6 WORD).
Reference) SM, S, C, T, AI, AQ memory of S7-200 PLC not support the bit write.
Analog Write
Analog write setting parameters are as follows:
1) Port Connected port number. (Not COM number)
2) Station Input PLC address between 0 and 126.
3) Address Output address of BYTE unit as decimal number
( But, in case of not using Read/Write address as BYTE unit, it is output address of BYTE/WORD/DWORD/FLOAT unit )
4) Extra1 Input among V.y, M.y, I.y, Q.y, SM.y, S.y, C, T, AI and AQ. ( Refer to <Table 1> )
y = Data type to read among blank, B, W, D and F
( B : BYTE, W or blank, etc : WORD, D : DWORD, F : FLOAT )
5) Extra2 Setting for writing/comparing Multi-analog value
1 = Save multi-write value, ( Don't care about Extar1 area )
2 = Write multi-write value as current saved value, ( Continuous output as much as the number of saved from current set address )
3 = Delete all contents which are saved by multi-write value, ( Don't care about Extar1 area )
4 = Compare PLC memory address value with current saved value, ( Continuous comparison as much as the number of saved from current set address )
Result of comparison is saved at designated WORD address of result of comparison. If comparison value is equal = 1, If comparison value is different = 0
Etc value( If value is larger than 0 or 4 ) = General( single ) analog value writing
Writing example 1)
Port : 0 Station : 0 Address : 0011, Extra1 : V.B, Extra2 : Blank
If you set as above and write analog value, you can change no.11 BYTE area of V memory as designated value(between 0 and 255).
Writing example 2)
Port : 0 Station : 0 Address : 0152, Extra1 : V.W, Extra2 : Blank
If you set as above and write analog value, you can change no.152 BYTE area(but, in case of not using Read/Write address as BYTE unit, it is no.152 WORD) of V memory as designated value(between 0 and 65535).
Writing example 3)
Port : 0 Station : 0 Address : 0035, Extra1 : V.D, Extra2 : Blank
If you set as above and write analog value, you can change no.35 BYTE area(but, in case of not using Read/Write address as BYTE unit, it is no.35 DWORD) of V memory as designated value(in range of DWORD data).
Writing example 4)
Port : 0 Station : 0 Address : 0176, Extra1 : V.F, Extra2 : Blank
If you set as above and write analog value, you can change no.176 BYTE area(but, in case of not using Read/Write address as BYTE unit, it is no.176 FLOAT) of V memory as designated value.
Writing example 5)
Port : 0 Station : 0 Address : 0016, Extra1 : M, Extra2 : Blank
If you set as above and write analog value, you can change no.16 BYTE area(but, in case of not using Read/Write address as BYTE unit, it is no.16 WORD) of M memory as designated value.
Reference) SM, S, C, T memory area of S7-200 PLC not support WORD unit write.
Example of writing script for Multi-Word writing settings)
$AO_0000.Extra2 = 3; // Delete previous saved multi-write value
@SetTagValue("AO_0000", 0);
$AO_0000.Extra2 = 1; // Set as saving multi-write value
for(i = 0; i < 105; i = i + 1) {
@sprintf($AO_0000.Extra1, "%03d", i); // Set as lest it ignore the same data by entering random value to Extra1
@SetTagValue("AO_0000", 5000); // Save real output value, random storage as 5000, in here
}
@sprintf($AO_0000.Extra1, "V.W"); // Memory designation, Set the memory type and unit of B ( Byte ), W ( Word ), D ( Dword ), F ( Float )
$AO_0000.Extra2 = 2; // Designate multi-value write
@SetTagValue("AO_0000", 1); // Write value, Output the 105 values from designated address
Example of writing script for confirming whether memory value and current value of PLC are same or not)
$AO_CHECK_MEM_SET = 2; // Set WORD address as 2, for confirming comparison completion
for(i = 0; i < 1; ) {
if($AI_CHECK_WRITE_STATUS == 2) i = 10; // Writing value of 2 is completed
@TagCheckLoop(); // Function for confirming tag value change
}
$AO_0000.Extra2 = 3; // Delete the previous saved data value
@SetTagValue("AO_0000", 0);
$AO_0000.Extra2 = 1; // Set as saving data value
for(i = 0; i < 105; i = i + 1) {
@sprintf($AO_0000.Extra1, "%03d", i); // Set as lest it ignore the same data by entering random value to Extra1
@SetTagValue("AO_0000", 5000); // Save real output value, random storage as 5000, in here
}
@sprintf($AO_0000.Extra1, "V.W"); // Memory designation, Set the memory type and unit of B ( Byte ), W ( Word ), D ( Dword ), F ( Float )
$AO_0000.Extra2 = 4; // Designate comparison of data value
@SetTagValue("AO_0000", 1); // Command for comparing data as much as input from designated address
for(i = 0; i < 1; ) {
if($AI_CHECK_WRITE_STATUS == 1) i = 10; // Compared result 1 = Same data
if($AI_CHECK_WRITE_STATUS == 0) { // Compared result 0 = Other data exists
@MessageBox("Contents of compared data are different each other.", "Data compared Error", MB_OK);
return;
}
@TagCheckLoop(); // Function for confirming tag value change
}
@MessageBox("Contents of compared data are same.", "Data compared Completion", MB_OK);
Note when you create a script for comparison)
1) Save result of comparison to WORD memory address which is set at Option part as 1 ( same data ) or 0 ( different data ).
2) Confirm result of comparison by first entering value except 1 and 0(value of 2, at example) to WORD address which is set before comparing PLC and memory.
3) Set the AO_CHECK_MEM_SET analog output tag so that write forcedly to WORD address which is set at Option part. ( Extra1 = Set as #MEM# )
4) Attune AI_CHECK_WRITE_STATUS analog input tag to WORD address which is set as PLC_SCAN tag.
Connect communication cable to SIEMENS S7-200 PLC, as follows.
RS-232C communication cable connection
Connect general RS-232C(Cross) cable to RS-232C terminal of SIEMENS S7-200 PLC such as <Figure 4>.
<Figure 4> is appearance of connecting RS-232C communication cable to SIEMENS S7-200 PLC.
 |
| <Figure 4> Appearance of connecting RS-232C communication cable to SIEMENS S7-200 PLC |