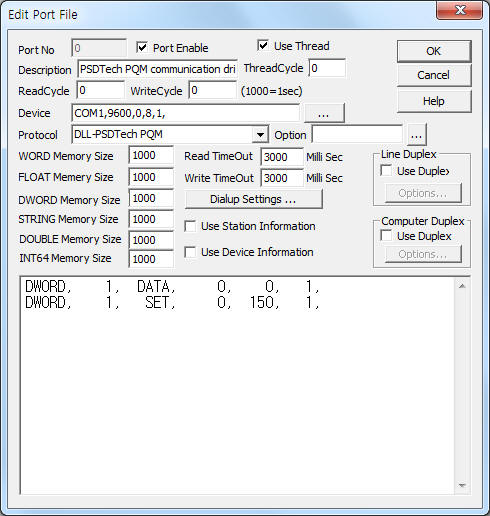
PSDTech PQM communication driver is the driver to communicate with Power Meter controller of PsdTech Co., Ltd. in Korea.
<Figure 1> is read setting example of PSDTech PQM communication driver.
 |
| <Figure 1> Read setting example of PSDTech PQM communication driver |
Device part of <Figure 1> input Com Port(COM1), Baud Rate(9600), Parity Bit(0), Data Bit(8), Stop Bit(1) respectively according to setting of controller.
Also you can set 'weather to calculate and save the readed data to Float'( 0 = don't calculate, 1 = calculate, default : 0) by using option part.
Station number and baud rate, ... can set by write setting or button of front panel.
PDTech PQM communication driver¡¯s read schedule
Read schedule setting parameters are as follows:
1) STATION – 0 ~ 255 station number of PQM controller.
2) Read command – command = DATA, VHD, SET, SAG. ( refer to <Table 1> ~ <Table 6> )
DATA – read of measurement data,
VHD – read of VHD measurement data,
SET – read of setting value,
SAG – read of Sag, Swell data.
3) Read start address – don't care.
4) Save Start Address for Communication Server – readed data saving start address of communication server.
5) Read Size – fixed to according to read command.
Read schedule example)
DWORD, 1, DATA, 0, 0, 1,
DWORD, 1, SET, 0, 150, 1,
Note) Station address of PQM controller can set by 'Analog write.
<Table 1> is data saving address and contents for DATA read command.
| Data saving address | Contents |
Remarks |
| Start addr + 0 ~ 5 | voltage of R phase, index voltage of S phase, index voltage of T phase, index |
E, index : default index refer to <Table 2> |
| Start addr + 6 ~ 7 | average voltage( E ) of 3 phase, index |
E |
| Start addr + 8 ~ 13 | voltage R-S phase, index voltage S-T phase, index voltage T-R phase, index |
V |
| Start addr + 14 ~ 15 | average voltage( V ) of 3 phase, index |
V |
| Start addr + 16 ~ 25 | current of R phase, index current of S phase, index current of T phase, index current of N phase, index current of 3 phase average, index |
A |
| Start addr + 26 ~ 33 | active power of R phase, index active power of S phase, index active power of T phase, index active power of 3 phase, index |
W |
| Start addr + 34 ~ 41 | apparent power of R phase, index apparent power of S phase, index apparent power of T phase, index apparent power of 3 phase, index |
VA |
| Start addr + 42 ~ 49 | fundamental wave reactive power of R phase, index fundamental wave reactive power of S phase, index fundamental wave reactive power of T phase, index fundamental wave reactive power of 3 phase, index |
VAr |
| Start addr + 50 ~ 57 | reactive power of R phase, index reactive power of S phase, index reactive power of T phase, index reactive power of 3 phase, index |
VAr |
| Start addr + 58 ~ 61 | PEAK, index DEMAND, index |
W |
| Start addr + 62 ~ 71 | K-factor of R phase, index K-factor of S phase, index K-factor of T phase, index K-factor of N phase, index K-factor of 3 phase, index |
|
| Start addr + 72 ~ 73 | distortion power of 3 phase, index |
|
| Start addr + 74 ~ 75 | emergency generator capacity of 3 phase, index |
Gh |
| Start addr + 76 ~ 77 | transformer single-phase load, index |
THDF-1¥õ |
| Start addr + 78 ~ 85 | transformer 3phase load of R phase, index transformer 3phase load of S phase, index transformer 3phase load of T phase, index transformer 3phase load of 3 phase, index |
THDF-1¥õ |
| Start addr + 86 ~ 93 | fower factor of R phase, index fower factor of S phase, index fower factor of T phase, index fower factor of 3 phase, index |
PF |
| Start addr + 94 ~ 101 | fundamental wave fower factor of R phase fundamental wave fower factor of S phase fundamental wave fower factor of T phase fundamental wave fower factor of 3 phase |
COS |
| Start addr + 102 ~ 109 | voltage unblanced factor of R phase, index voltage unblanced factor of S phase, index voltage unblanced factor of T phase, index voltage unblanced factor of 3 phase, index |
% |
| Start addr + 110 ~ 117 | current unblanced factor of R phase, index current unblanced factor of S phase, index current unblanced factor of T phase, index current unblanced factor of 3 phase, index |
% |
| Start addr + 118 ~ 119 | HZ, index |
|
| Start addr + 120 ~ 123 | TR temperature, index PANNEL temperature, index |
¡É |
| Start addr + 124 ~ 117 | 3phase amount of active power( KWh ), index 3phase amount of reactive power( KvArh ), index |
index : refer to <Table 3> |
| Start addr + 128 | alarm status |
bit 0 : TRT bit 1 : MCSGT bit 2 : PEAK bit 3 : VTHD bit 4 : OCR bit 5 : UNB bit 6 : PF bit 7 : V.CUR |
| Start addr + 129 | INPUT status |
bit 0 : Â÷´Ü±â bit 1 : OCR bit 2 : OCGR bit 3 : ELD |
| Start addr + 130 ~ 134 | year, month, day, hour, minute |
each 2digit data (0 ~ 99 year) |
| <Table 1> Data saving address and contents for DATA read command | ||
<Table 2>, <Table 3> are unit and decimal point for default, amount of active power Index.
Index |
Unit |
Decimal point |
0 |
m(mili) |
2 |
1 |
1 |
|
2 |
(unit) |
3 |
3 |
2 |
|
4(0) |
1 |
|
5 |
K(Kilo) |
3 |
6 |
2 |
|
7 |
1 |
|
8 |
M(Mega) |
3 |
9 |
2 |
|
10 |
1 |
|
| <Table 2> Unit and decimal point for default Index ( include PT, CT ratio ) | ||
Index |
Unit |
Decimal point |
0 |
KWH(KVARH) |
3 |
1 |
2 |
|
2 |
1 |
|
3 |
0 |
|
| <Table 3> Unit and decimal point for amount of active power Index | ||
<Table 4> ~ <Table 6> are data saving address and contents for VHD, SET, SAG read command.
| Data saving address | Contents |
Remarks |
| Start addr + 0 ~ 51 | V-1 harmonic( V ) of R phase, index V-3 harmonic( % ) of R phase, index ¡¦ V-21 harmonic( % ) of R phase, index |
26 harmonic data for each harmonic |
| Start addr + 52 ~ 103 | V-1 harmonic( V ) of S phase, index V-3 harmonic( % ) of S phase, index ¡¦ V-21 harmonic( % ) of S phase, index |
|
| Start addr + 104 ~ 155 | V-1 harmonic( V ) of T phase, index V-3 harmonic( % ) of T phase, index ¡¦ V-21 harmonic( % ) of T phase, index |
|
| Start addr + 156 ~ 207 | A-1 harmonic( A ) of R phase, index A-3 harmonic( % ) of R phase, index ¡¦ A-21 harmonic( % ) of R phase, index |
|
| Start addr + 208 ~ 259 | A-1 harmonic( A ) of S phase, index A-3 harmonic( % ) of S phase, index ¡¦ A-21 harmonic( % ) of S phase, index |
|
| Start addr + 260 ~ 311 | A-1 harmonic( A ) of T phase, index A-3 harmonic( % ) of T phase, index ¡¦ A-21 harmonic( % ) of T phase, index |
|
| Start addr + 312 ~ 363 | A-1 harmonic( A ) of N phase, index A-3 harmonic( % ) of N phase, index ¡¦ A-21 harmonic( % ) of N phase, index |
|
| Start addr + 364 ~ 371 | V ( THD ) % of R phase, index V ( THD ) % of S phase, index V ( THD ) % of T phase, index V ( THD ) average % of 3 phase, index |
|
| Start addr + 372 ~ 381 | A ( THD ) % of R phase, index A ( THD ) % of S phase, index A ( THD ) % of T phase, index A ( THD ) % of N phase, index A ( THD ) % of 3 phase average, index |
|
| Start addr + 382 ~ 391 | ITDD of R phase, index ITDD of S phase, index ITDD of T phase, index ITDD of N phase, index ITDD of 3 phase average, index |
|
| <Table 4> Data saving address and contents for VHD read command | ||
| Data saving address | Contents |
Remarks |
| Start addr + 0 ~ 3 | PT 1 value, index PT 1 value, index |
|
| Start addr + 4 ~ 7 | CT 1 value, index CT 1 value, index |
|
| Start addr + 8 | wiring method |
1 : DA - 3P3W 2 : 3P4W 3 : 1P2W 4 : 1P3W |
| Start addr + 9 ~ 13 | year, month, day, hour, minute of current time |
|
| Start addr + 14 ~ 15 | TR temperature, PANEL temperature |
|
| Start addr + 16 | voltage THD |
|
| Start addr + 17 ~ 18 | over current, index |
|
| Start addr + 19 | unblanced factor |
|
| Start addr + 20 ~ 21 | neutral current, index |
|
| Start addr + 22 ~ 23 | PEAK, index |
|
| Start addr + 24 ~ 25 | DEMAND, index |
|
| Start addr + 26 | power factor |
|
| Start addr + 27 | type of transformer |
1 - Dry 1MVA below 2 - Dry 1MVA excess 3 - Oil-Filled 2.5MVA below 4 - Oil-Filled 2.5MVA excess 5MVA below 5 - Oil-Filled 5MVA excess |
| <Table 5> Data saving address and contents for SET read command | ||
| Data saving address | Contents |
Remarks |
| Start addr + 0 | item of R phase |
0 : normal, ( Sag, Swell not occured ) 1 : Sag (voltage RMS = 0.5 cycle¡1 minute under, 10¡90% decrease) 2 : Undervoltage (voltage RMS = 1minute over, 10¡90% decrease) 3 : Interruption (voltage RMS = 0.5 cycle¡1 minute under, 10% under decrease) 4 : Swell (voltage RMS = 0.5 cycle¡1 minute under, 110% over increase) 5 : Overvoltage (voltage RMS = 1 minute over, 110% over increase) |
| Start addr + 1 ~ 6 | occurrence year, month, day, hour, minute, second of R phase |
|
| Start addr + 7 | cycle or minute for R phase |
'1'[Sag], '3'[Interruption], '4'[Swell] : cycle ¡®2¡¯[Undervoltage], '5'[Overvoltage] : minute |
| Start addr + 8 ~ 9 | voltage RMS % value of R phase, index |
|
| Start addr + 10 | item of S phase |
same as R phase |
| Start addr + 11 ~ 16 | occurrence year, month, day, hour, minute, second of S phase |
|
| Start addr + 17 | cycle or minute for S phase |
same as R phase |
| Start addr + 18 ~ 19 | voltage RMS % value of S phase, index |
|
| Start addr + 20 | item of T phase |
same as R phase |
| Start addr + 21 ~ 26 | occurrence year, month, day, hour, minute, second of T phase |
|
| Start addr + 27 | cycle or minute for T phase |
same as R phase |
| Start addr + 28 ~ 29 | voltage RMS % value of T phase, index |
|
| <Table 6> Data saving address and contents for SAG read command | ||
Note) All index value of <Table 1>, <Table 4>, <Table 5>, <Table 6> use the value of <Table 2> except active power Index.
PSDTech PQM communication driver store the same data in WORD, DWORD, FLOAT( when using 'weather to calculate and save the readed data to Float' option ) memory, but the data format are different.
If you click the icon ![]() in protocol option part, you
can see the dialog box such as <Figure 2>. you can also set read schedule by
using this part.
in protocol option part, you
can see the dialog box such as <Figure 2>. you can also set read schedule by
using this part.
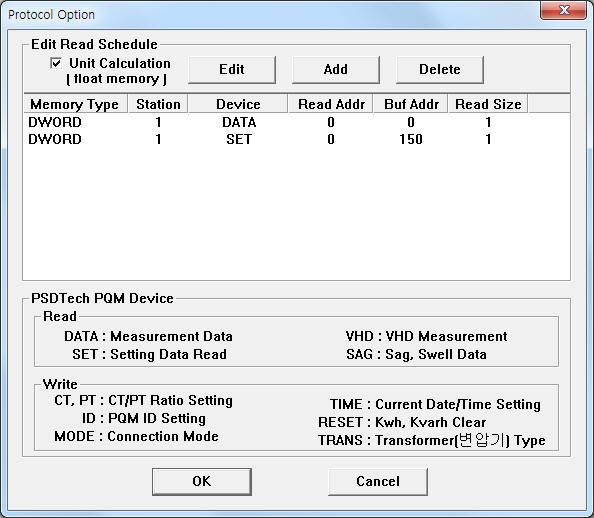 |
| <Figure 2> Example of PSDTech PQM communication driver¡¯s Option dialog box |
You can set read schedule by using ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() button and listbox of <Figure
2>.
button and listbox of <Figure
2>.
Also, you can set weather to calculate and save the readed data to Float by using the part of ¡®Unit Calculation' shown in <Figure 2>.
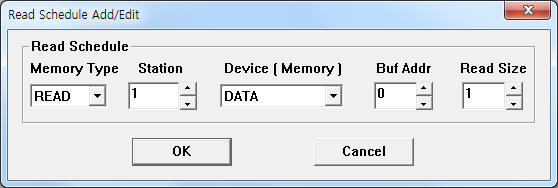 |
| <Figure 3> Example of PSDTech PQM communication driver¡¯s read schedule Add/Edit dialog box |
When you click Add button or Edit button in dialog box of <Figure 2>, dialog box of <Figure 3> is shown.
You can control PQM controller by using write settings.
Digital Write
Digital write setting parameters are as follows:
1) PORT Port no. (0 ~ 255)
2) STATION 0 ~ 255 station number of PQM controller.
3) ADDRESS type selection of PC, CT ration when PC, TC write command.
0 = PT 1, CT 1 ratio setting,
1 = PT 1, CT 1 index setting,
2 = PT 2, CT 2 ratio setting,
3 = PT 2, CT 2 index setting.
4) Extra1 write command = PT, CT, TIME, ID, RESET, MODE, TRANS, ...
PT, CT : PT, CT ratio/ index setting,
TIME : time syncronization with computer,
ID : station ID number setting of PQM controller,
RESET : clear command for 3 phase amount of active power( Kwh ), 3 phase amount of reactive power( Kvarh ) Clear,
( output value - 1 = 3 phase amount of active power clear, 2 = 3 phase amount of active power clear clear )
MODE : setting of wiring method, ( output value - 1= DA - 3P3W, 2 = 3P4W, 3 = 1P2W, 4 = 1P3W )
TRANS : selection of transformer type.
( output value - 1 = Dry 1MVA below, 2 = Dry 1MVA excess, 3 = Oil-Filled 2.5MVA below, 4 = Oil-Filled 2.5MVA excess 5MVA below, 5 = Oil-Filled 5MVA excess )
5) Extra2 don't care.
Write example 1)
PORT:0, station:1, ADDRESS:0000, Extra1: TIME, Extra2 :
The setting parameter shown above is time syncronization example with computer for 1 station number PQM controller.
Analog Write
Analog write and digital write have the same setting parameters except output value.
Write example 1)
PORT:0, station:2, ADDRESS:0000, Extra1: TIME, Extra2 :
The setting parameter shown above is time syncronization example with computer for 2 station number PQM controller.
Write example 2)
PORT:0, station:1, ADDRESS:0000, Extra1: PT, Extra2 :
The setting parameter shown above is PT 1 ratio setting example for station number 1 PQM controller.
Write example 3)
PORT:0, station:1, ADDRESS:0001, Extra1: PT, Extra2 :
The setting parameter shown above is PT 1 index setting example for station number 1 PQM controller.
Write example 4)
PORT:0, station:1, ADDRESS:0002, Extra1: PT, Extra2 :
The setting parameter shown above is PT 2 ratio setting example for station number 1 PQM controller.
Write example 5)
PORT:0, station:1, ADDRESS:0000, Extra1: CT, Extra2 :
The setting parameter shown above is CT 1 ratio setting example for station number 1 PQM controller.
Write example 6)
PORT:0, station:1, ADDRESS:0000, Extra1: RESET, Extra2 : , Output value = 1
The setting parameter shown above is 3 phase amount of active power clear ( to 0 ) setting example for station number 1 PQM controller.
Write example 7)
PORT:0, station:1, ADDRESS:0000, Extra1: RESET, Extra2 : , Output value = 2
The setting parameter shown above is 3 phase amount of reactive power clear ( to 0 ) setting example for station number 1 PQM controller.
Write example 8)
PORT:0, station:1, ADDRESS:0000, Extra1: MODE, Extra2 :
The setting parameter shown above is wiring method setting example for station number 1 PQM controller. ( output value = 1 ~ 4 )
Write example 9)
PORT:0, station:1, ADDRESS:0000, Extra1: TRANS, Extra2 :
The setting parameter shown above is transformer type setting example for station number 1 PQM controller. ( output value = 1 ~ 5 )
Write example 10)
PORT:0, station:1, ADDRESS:0000, Extra1: ID, Extra2 :
The setting parameter shown above is station ID number setting example for station number 1 PQM controller. ( output value = 0 ~ 2555 )
Please connect RS-485 communication cable to +, - connector of PQM controller.
RS- 485 of computer RS-485 connector of PQM controller
Tx+, Rx+ --------------------------------- + ( 5th connector from above )
Tx-, Rx- ---------------------------------- - ( 5th connector from above )
Note) Please use RS-485 communication converter supported by Tx, Rx flow control at hardware. ( It is recommended that you use the RS-485 converter of PSDTech )
<Figure 4> is connection example of communication cable to PQM controller.
<Figure 5> is appearance of PQM controller.
<Figure 6> is appearance of PQM display and setting controller.
 |
| <Figure 4> Connection example of communication cable to PQM controller |
 |
| <Figure 5> Appearance of PQM controller |
 |
| <Figure 6> Appearance of PQM display and setting controller |