OMRON SYSMAC Ethernet communication driver is the driver to communicate with PLC( ethernet module ) of OMRON Corporation in Japan.
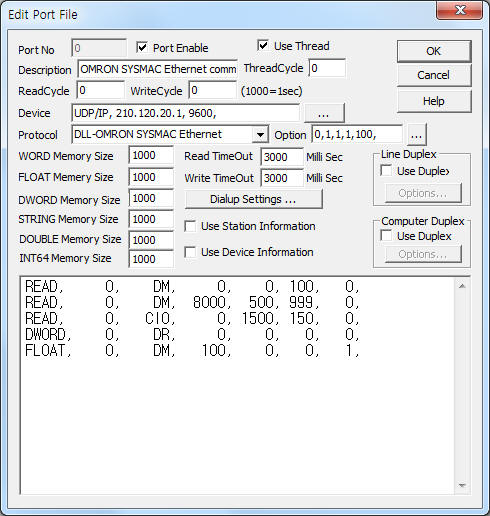
<Figure 1> is read setting example of OMRON SYSMAC Ethernet communication driver.
 |
| <Figure 1> Read setting example of OMRON SYSMAC Ethernet communication driver |
Device part of <Figure 1> input Device type(UDP/IP or TCP/IP), IP address of PLC(210.120.20.1), service port of UDP/IP ( or TCP/IP ) protocol ( 9600 ),respectively, according to setting of PLC.
In protocol option part, you can set CPU type( 0 = CS/CJ, 1 = CV, default = 0 ), Network address of PLC( 1 ~ 127, default = 1 ), Network address of computer( 1 ~ 127, default = 1), Node address of computer( 1 ~ 126, default = 100 ). Each argument is a comma-delimited.
Note) Please refer to manual of OMRON PLC or chapter 3 for Network, Node address....
Note) You can set IP address and Node address by using 'Cx-Programmer'.
If don't matck IP address or Node address, ¡°Write Not Possible¡±(Main Error = 21, Sub Error = 08) error will occur.
Also, ¡°Command Format Error¡± will occur when 'Unit number' incorrectly set.
OMRON SYSMAC Ethernet communication driver read schedule
Read schedule setting parameters are as follows:
1) Unit number – PLC unit number( 0~47, ... ).
0 = CPU Unit, 16 ~ 31 = CPU Bus Unit 0 ~ 15, E1 = Inner Board, FE = Unit Connected to Network.
2) Read memory type – memory type = CIO, WR, HR, AR, TF, CF, TIM, CNT, DM, EM0 ~ EMC, EM, EM_CURR, TKF, TK, IR, DR, CLOCK, CONDITION,... ( refer to <Table 1> )
3) Read start address – read start address in memory type.
4) Save start address for Communication Server – Saving start address of Communication Server.
5) Read size – read size. word memory area = 1 ~ 999, byte, bit memory area = 1 ~ 1980.
6) Unit of float data – 0 = word, double word unit, 1 = float unit.
Read schedule example)
READ, 0, DM, 0, 0, 100,
READ, 0, DM, 8000, 500, 999,
READ, 0, CIO, 0, 1500, 150,
DWORD, 0, DR, 0, 0, 16,
FLOAT, 0, DM, 100, 0, 25, 1, 0,
<Table 1> is memory type and range of OMRON PLC.
<Table 2>, <Table 3> are address and contents of CLOCK/CONDITION memory type.
| Memory type | Data type | Memory range of CS/CJ CPU | Memory range of CV CPU | Remarks |
| CIO | WORD | 0 ~ 6143 | 0 ~ 2555 | |
| WR | 0 ~ 511 | - | ||
| HR | - | |||
| AR | 0 ~ 959 | 0 ~ 959 | 0 ~ 447 = read only, 448 ~ 959 = read/write |
|
| TF | Completion Flag( BIT ) | 0 ~ 4095 | 0 ~ 2047 ¶Ç´Â 0 ~ 1023 |
read only |
| CF | ||||
| TIM | WORD | |||
| CNT | ||||
| DM | 0 ~ 32767 | 0 ~ 32767 | ||
| EM0 ~ EM7 | ||||
| EM8 ~ EMC | - | |||
| EM | 0 ~ 32767 | |||
| EM_CURR | exist only '0' address | - | read only | |
| TKF | BIT | 0 ~ 1023 | - | |
| TK | Status | - | ||
| IR | DWORD | 0 ~ 15 | - | |
| DR | WORD | 0 ~ 15 | ||
| CLOCK | BIT | 0 ~ 4 | - | read only can read only by 1 item |
| CONDITION | 0 ~ 16 | - | ||
| <Table 1> Memory type and range of OMRON PLC | ||||
| Address | Contnets | Remarks |
| 0 | 1minute Clock | 30second – ON, 30second – OFF |
| 1 | 1second Clock | 0.5second – ON, 0.5second – OFF |
| 2 | 0.2second Clock | 0.1second – ON, 0.1second – OFF |
| 3 | 0.1second Clock | 0.05second – ON, 0.05second – OFF |
| 4 | 0.02second Clock | 0.01second – ON, 0.01second – OFF |
| <Table 2> Address and contents of CLOCK memory type | ||
| Address | Contnets |
| 0 | Error Flag ( ER ) |
| 1 | Carry Flag ( CF ) |
| 2 | Greater Than Flag ( > ) |
| 3 | Equals Flag ( = ) |
| 4 | Less Then Flag ( < ) |
| 5 | Negative Flag ( N ) |
| 6 | Overflow Flag ( OF ) |
| 7 | Underflow Flag ( UF ) |
| 8 | Greater Then or Equals Flag ( >= ) |
| 9 | Not Equal Flag ( <> ) |
| 10 | Less Then or Equals Flag ( <= ) |
| 14 | Always OFF Flag ( ON ) |
| 15 | Always ON Flag ( OFF ) |
| 16 | Access Error Flag |
| <Table 3> Address and contents of CONDITION memory type | |
Note) BIT memory type of OMRON PLC( refer to <Table 1> ) can be read 1980 data at a time. The readed value save 0 bit at each WORD memory of Communication Server. ( protocol data = BYTE value ).
If you click the icon ![]() in protocol option part at
<Figure 1>, you
can see the dialog box such as <Figure 2>. you can also set read schedule by
using this part.
in protocol option part at
<Figure 1>, you
can see the dialog box such as <Figure 2>. you can also set read schedule by
using this part.
 |
| <Figure 2> Example of OMRON SYSMAC Ethernet communication driver¡¯s Option dialog box |
You can set read schedule by using ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() button and listbox of <Figure
2>.
button and listbox of <Figure
2>.
Also, you can set CPU type, Network address of PLC, Network address of computer, Node address of computer by using the part of ¡®Cpu Type¡¯, 'PLC Communication Address', 'PC Communication Address' shown in <Figure 2>.
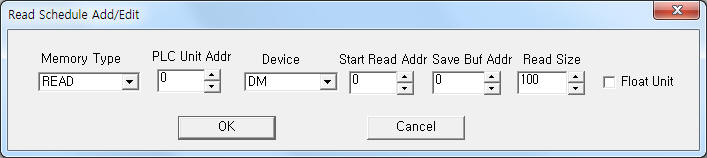 |
| <Figure 3> Example of OMRON SYSMAC Ethernet communication driver¡¯s read schedule Add/Edit dialog box |
When you click Add button or Edit button in dialogue box of <Figure 2>, dialogue box of <Figure 3> is shown.
You can set OMRON SYSMAC PLC by using 'write settings'.
Digital Write
Digital write setting parameters are as follows:
1) PORT Port no. (0 ~ 255)
2) STATION PLC unit number( 0~47, ... ).
0 = CPU Unit, 16 ~ 31 = CPU Bus Unit 0 ~ 15, E1 = Inner Board, FE = Unit Connected to Network.
3) ADDRESS data writing address in memory type.
higher 1 ~ 7 digit : decimal unit word address,
lower 1 digit : 0 ~ F bit position. ( hex-decimal unit )
4) Extra1 write memory type = CIO, WR, HR, AR, TIM, CNT, DM, EM0 ~ EMC, EM, IR, DR. ( refer to <Table 1> )
5) Extra2 don't care.
Write example 1)
PORT:0, station:0, ADDRESS:0003, Extra1:CIO, Extra2 : 0
The setting parameter shown above is bit write control( On/Off ) example for 0 word, 3 bit of CIO memory.
Write example 2)
PORT:0, station:0, ADDRESS:448F, Extra1:AR, Extra2 : 0
The setting parameter shown above is bit write control( On/Off ) example for 448 word, F bit of AR memory.
Write example 3)
PORT:0, station:0, ADDRESS:0257, Extra1:DM, Extra2 : 0
The setting parameter shown above is bit write control( On/Off ) example for 25 word, 7 bit of DM memory.
Analog Write
Analog write setting parameters are as follows:
1) PORT Port no. (0 ~ 255)
2) STATION PLC unit number( 0~47, ... ).
0 = CPU Unit, 16 ~ 31 = CPU Bus Unit 0 ~ 15, E1 = Inner Board, FE = Unit Connected to Network.
3) ADDRESS data writing address in memory type.
4) Extra1 writte memory type = CIO, WR, HR, AR, TIM, CNT, DM, EM0 ~ EMC, EM, IR, DR. ( refer to <Table 1> )
5) Extra2 selection writing data type.
0 = word/double word data,
1 = float data.
Note) You can read and write by float only 'word', 'double word' memory area
Also, float data calculate 'IEEE754' format from 2 word.
Write example 1)
PORT:0, station:0, ADDRESS:0005, Extra1:CIO, Extra2 : 0
The setting parameter shown above is word write example for 5 word of CIO memory.
Write example 2)
PORT:0, station:0, ADDRESS:0450, Extra1:AR, Extra2 : 0
The setting parameter shown above is word write example for 450 word of AR memory.
Write example 3)
PORT:0, station:0, ADDRESS:32767, Extra1:DM, Extra2 : 0
The setting parameter shown above is word write example for 32767 word of DM memory.
Block Write
Block write use PlcScanWriteBlock script such as follows.
script function and parameters : @PlcScanWriteBlock(int port, int station, int address, string extra1, string extra2, object array_value, int array_size);
(max 256 word, 128 double word/Float, Float data : Extra2 = 1 )
Block write script example 1 ( DM memory Block Write )
ushort Val[10];
Val[0] = 25;
Val[1] = 55;
Val[2] = 31;
Val[3] = 2347;
Val[4] = 3869;
Val[5] = 5;
Val[6] = 72;
Val[7] = 32756;
Val[8] = 541;
Val[9] = 8845;
@PlcScanWriteBlock(0, 0, 0, "DM", 0,
Val, 10);
Block write script example 1 ( DM memory float unit Block Write )
float Val[10];
Val[0] = 12286.2;
Val[1] = 255.5;
Val[2] = 32.45;
Val[3]
= 400.567;
Val[4] = 65.12;
Val[5] = 1026.9;
Val[6] = 327.1;
Val[7] =
3.5;
Val[8] = 4.9;
Val[9] = 91.56;
@PlcScanWriteBlock(0, 0, 0, "DM",
1, Val,
10);
Settings of main power and Ethernet communication module are as follows :
Connection of main power
Please connect 100 ~ 240V AC main power to power input connector such as <Figure 4>.
 |
| <Figure 4> Connection example of main power and communication cable to CS/CJ module ONRON PLC |
Setting of Ethernet communication module
Please set Unit, Node address by suing DIP switch.
Unit address : set 0 ~ F Unit address by using upper DIP switch.
Node address : set 1 ~ 126 Node address by using lower 2 DIP switch.
Setting of Network, Node for PLC and computer
You can set IP address and Node address by using 'Cx-Programmer'. ( Network address = 1 ~ 127, Node address = 1 ~ 126 )
<Table 4> is address setting range and contents for OMRON PLC Ethernet.
| Item | Range | Contents |
| Network address | 1 ~ 127 | set equal Netwrok address PLC and computer |
| Node address | 1 ~ 126 | set different Node address PLC and computer |
| Unit address | 0, 16 ~ 31, E1, FE | 0 = CPU Unit, 16 ~ 31 = CPU Bus Unit 0 ~ 15, E1 = Inner Board, FE = Unit Connected to Network |
| <Table 4> Address setting range and contents for OMRON PLC Ethernet | ||
IP address setting
Please set IP address of PLC by using 'Cx-Programmer'. ( provided by OMRON )
Settings for OMRON Ethernet is as follows :
1) Condition of Ethernet Test
<Figure 5> is Set Up order diagram for Ethernet setting.
 |
| <Figure 5> Set Up order diagram for Ethernet setting |
2) Setting of Ethernet Unit
Please set OMRON Ethernet module such as <Figur 6>.
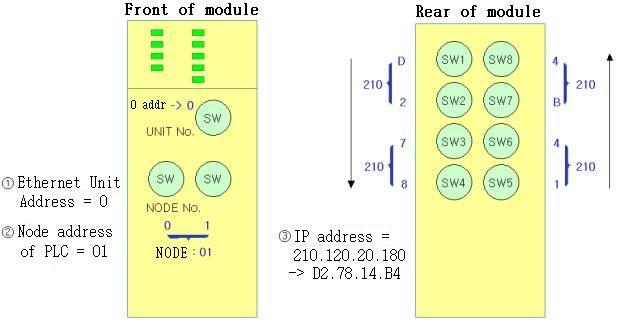 |
| <Figure 6> Diagram of OMRON Ethernet module |
* Please use end 2 digit DIP switch for IP Address setting when using 'automatic setting' Address converting.
* Please equally set switch 7, 8 and Node addresswhen using 'automatic generation' Address converting.
If the values are different, ERC LED is turned on. ( No relationship when Combination and Table method, example = Table method )
3) Setting of Routing Table
You can set Routing Table such as <Figure 7>.
 |
| <Figure 7> Setting example of Routing Table |
4) Create New Project
You can create 'New Project' such as <Figure 8>, <Figure 9>, <Figure 10>, <Figure 11>.
 |
| <Figure 8> Example of Create New Project |
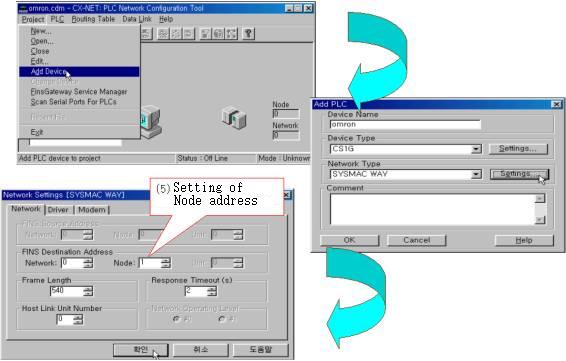 |
| <Figure 9> Setting example for PLC type and Node address |
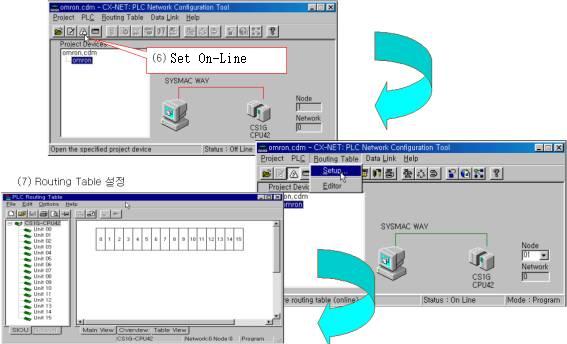 |
| <Figure 10> Setting example for On-Line and Routing Table |
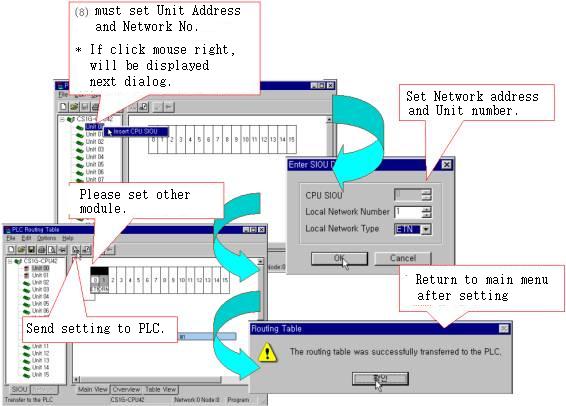 |
| <Figure 11> Setting example for each module |
4) Setting of I/O Table
I/O Table can set such as <Figure 12>.
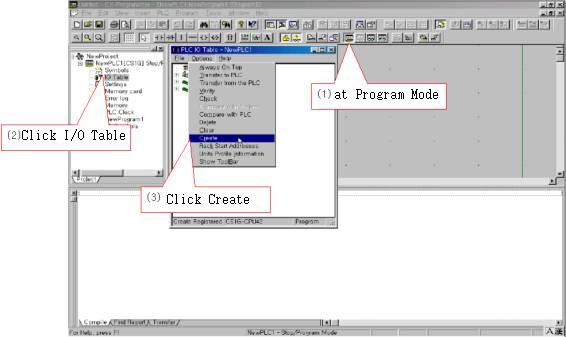 |
| <Figure 12> Setting example for I/O Table |
5) Setting of Ethernet Unit
Ethernet Unit can set such as <Figure 13>, <Figure 14>, <Figure 15>.
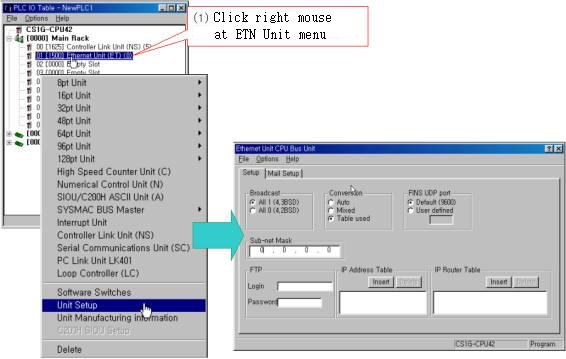 |
| <Figure 13> Setting example for Ethernet Unit |
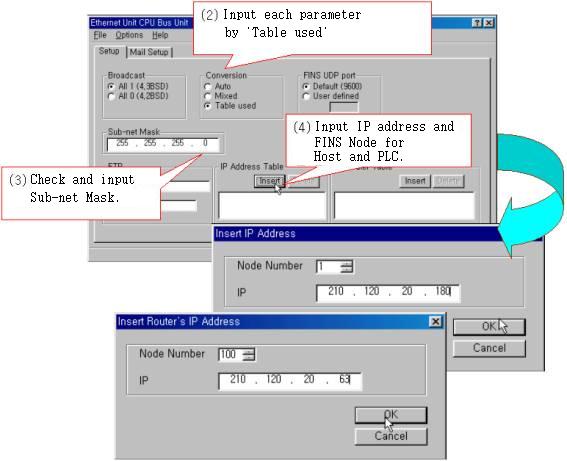 |
| <Figure 14> Dialog example of IP address and FINS Node address |
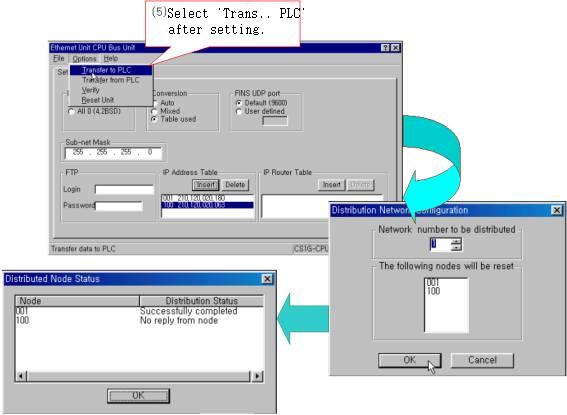 |
| <Figure 15> Example of 'Transfer to PLC' |
6) Online method at Cx-Programmer
Online method of Cx-Programmer is such as <Figure 16>, <Figure 17>, <Figure 18>.
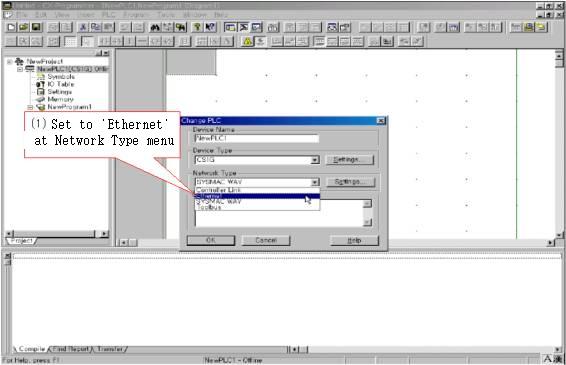 |
| <Figure 16> Setting example of 'Network Type' |
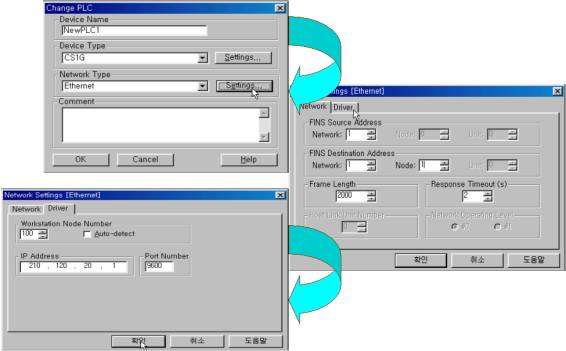 |
| <Figure 17> Setting example forNetwork |
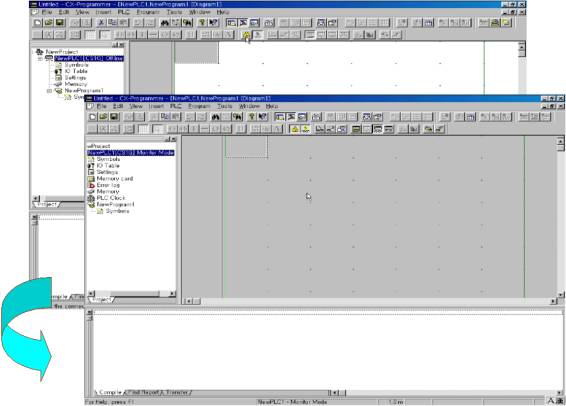 |
| <Figure 18> Appearance of 'Cx-Programmer' |