MELSEC ENET 3E communication driver is the driver to communicate with MJ71QE71, QJ71E71 module of MELSEC PLC of Mitsubishi in Japan.
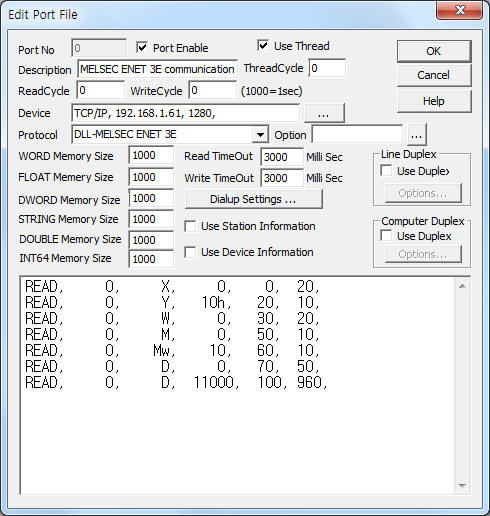
<Figure 1> is read setting example of MELSEC ENET 3E communication driver.
 |
| <Figure 1> Read setting example of MELSEC ENET 3E communication driver |
Device part of <Figure 1> input Device type(TCP/IP), IP address of PLC(192.168.1.61), service port of TCP/IP protocol ( 1280 ),respectively, according to setting of PLC.
In protocol option part, you can set the following: number of monitoring computer(255 or 1 ~ 64), number of Destination Module I/O(single PLC : 1023, ... ), number of Destination Module Station(default = 0), whether or not point rounding when word writing(rounding : 1, don't rounding : 0, defualt = 0). Each argument is a comma-delimited.
number of monitoring computer (PC number) : 255 or 1 ~ 64,
number of Destination Module I/O : single PLC system – 1023 (03FFh),
PLC 1 - 992 (03E0h), PLC 2 – 993 (03E1h), PLC 3 - 994 (03E2h), PLC 4 – 995 (03E3h),
Multi Drop – 0 ~ 511 (01FF).
number of Destination Module Station : single PLC – 0,
Multi Drop – 0 ~ 31 (01F).
Note) When a communication error about TCP/IP connection occurs, the problem can be solved as follows.
1) Make 2 or more TCP/IP (or UDP/IP) service port routine in the Ladder program.
2) Input service port number at 'Device' part of <Figure 1> such as 1280, 1281, 1282 ¡¦(service port number = made by ladder program).
3) It can slove TCP/IP connection problem by connecting the next service port.
MELSEC ENET 3E communication driver read schedule
Read schedule setting parameters are as follows:
1) Station – 0 ~ 255 station number of PLC. direct connection = 0, other = according to setting switch.
2) Read memory type – memory type = B, CC, CCw, CN, CS, CSw, D, DX, DY, F, Fw, L, Lw, M, Mw, R, S, S w, SB, SC, SCw, SD, SM, SMw, SN, SS, SSw, SW, TC, TCw, TN, TS, TSw, V, Vw, W, X, Y, Z, ZR. ( refer to <Table 1> )
3) Read start address – reading start address in memory.
X, Y, B memory = read start address x 16.
4) Save start address for Communication Server – Saving start address of Communication Server.
5) Read Size – read size( word or 10 bit unit ).
Q Series - word unit : 1 ~ 960, 10bit unit : 1 ~ 790,
A Series, ... - word unit : 1 ~ 480, 10bit unit : 1 ~ 395,
other - word unit : 1 ~ 32, 10bit unit : 1 ~ 25.
Read schedule example)
READ, 0, X, 0, 0, 20,
READ, 0, Y, 10h, 20, 10,
READ, 0, W, 0, 30, 20,
READ, 0, M, 0, 50, 10,
READ, 0, Mw, 10, 60, 10,
READ, 0, D, 0, 70, 50,
READ, 0, D, 11000, 100, 960,
READ, 0, DF2, 10, 60, 5,
READ, 0, DD2, 10, 60, 5,
Note) 10h = hex-dicimal unit. ( above example )
<Table 1> is memory type and contents of Q series PLC.
| Memory type | Contents of memory | Bit write | Read/Write command | read unit | Address | Remarks |
| B | LINK relay | O | B | WORD | hex-decimal | * read size = 1 word unit = 16 bit(1 word ), 10bit unit = 10 bit Digital write for CN, D, R, TN, W = bit operation after word unit reading. |
| CC | Counter | O | CC | 10 BIT | decimal | |
| CCw | WORD | |||||
| CN | X | CN | WORD | |||
| CS | O | CS | 10 BIT | |||
| CSw | WORD | |||||
| D | DATA register | X | D | WORD | ||
| DF2 | FLOAT | |||||
| DD2 | DWORD | |||||
| DX | Direct Input | O | DX | WORD | hex-decimal | |
| DY | Direct Output | DY | WORD | |||
| F | ANNUNCIATOR | O | F | 10 BIT | decimal | |
| Fw | WORD | |||||
| L | LATCH relay | O | L | 10 BIT | ||
| Lw | WORD | |||||
| M | Internal relay | O | M | 10 BIT | ||
| Mw | WORD | |||||
| R | FILE register | X | R | WORD | ||
| S | STEP relay | O | S | 10 BIT | ||
| S w | WORD | |||||
| SB | Special Link relay | O | SB | WORD | hex-decimal | |
| SC | Retentive timer | O | SC | 10 BIT | decimal | |
| SCw | WORD | |||||
| SN | X | SN | WORD | |||
| SS | O | SS | 10 BIT | |||
| SSw | WORD | |||||
| SD | Special gerister | X | SD | WORD | ||
| SM | STEP relay | O | SM | 10 BIT | ||
| SMw | WORD | |||||
| SW | Special LINK register | O | SW | WORD | hex-decimal | |
| TC | Timer | O | TC | 10 BIT | decimal | |
| TCw | WORD | |||||
| TN | X | TN | WORD | |||
| TS | O | TS | 10 BIT | |||
| TSw | WORD | |||||
| V | EDGE relay | O | V | 10 BIT | ||
| Vw | WORD | |||||
| W | LINK resister | X | W | WORD | hex-decimal | |
| X | Input relay | O | X | WORD | ||
| Y | Output relay | Y | WORD | |||
| Z | INDEX register | X | Z | WORD | decimal | |
| ZR | FILE register(Serial NO. Access) | O | ZR | WORD | hex-decimal | |
| <Table 1> Memory type and contents of Q series PLC | ||||||
If you click the icon ![]() in protocol option part at
<Figure 1>, you
can see the dialogue box such as <Figure 2>. you can also set read schedule by
using this part.
in protocol option part at
<Figure 1>, you
can see the dialogue box such as <Figure 2>. you can also set read schedule by
using this part.
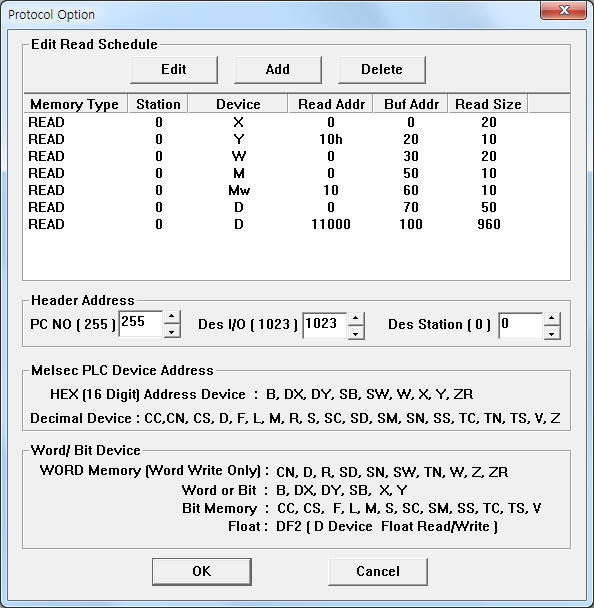 |
| <Figure 2> Example of MELSEC ENET 3E communication driver¡¯s Option dialog box |
You can set read schedule by using ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() button and listbox of <Figure
2>.
button and listbox of <Figure
2>.
Also, you can set set monitoring computer number, number of Destination Module I/O, number of Destination Module Station by using the part of 'PC NO', 'DES I/O', 'Des Station' shown in <Figure 2>.
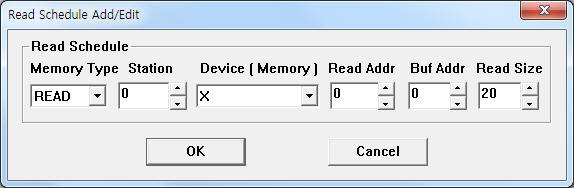 |
| <Figure 3> Example of MELSEC ENET 3E communication driver¡¯s read schedule Add/Edit dialog box |
When you click Add button or Edit button in dialogue box of <Figure 2>, dialogue box of <Figure 3> is shown.
You can set Melsec PLC by using 'writing settings'.
Digital Write
Digital write setting parameters are as follows:
( CN, D, R, SD, SN, SW, TN, W, Z, ZR = bit operation after word unit reading )
1) PORT Port no. (0 ~ 255)
2) STATION station number of PLC. ( single PLC = 255 )
3) ADDRESS address in PLC memory.
B, DX, DY, SB, SW, W, X, Y, ZR = hex-decimal unit,
other = decimal unit.
4) Extra1 write memory type = B, CC, CN, CS, D, DX, DY, F, L, M, R, S, SB, SC, SD, SM, SN, SS, SW, TC, TN, TS, V, W, X, Y, Z, ZR.
5) Extra2 don't care.
Write example 1)
PORT:0, station:255, ADDRESS:001A, Extra1: Y, Extra2 : 0
The setting parameter shown above is bit control(On/Off) example for Y001A address ( bit unit ) of Y memory.
Write example 2)
PORT:0, station:255, ADDRESS:0100, Extra1: M, Extra2 : 0
The setting parameter shown above is bit control(On/Off) example for 100 address ( bit unit ) of M memory.
Analog Write
Analog write setting parameters are as follows:
1) PORT Port no. (0 ~ 255)
2) STATION station number of PLC. ( single PLC = 255 )
3) ADDRESS address in PLC memory.
B, DX, DY, SB, SW, W, X, Y, ZR = hex-decimal unit,
other = decimal unit. ( CC, CS, F, L, M, S, SC, SM, SS, TC, TS, V : bit memory = 16 bit write )
4) Extra1 write memory type = B, CC, CN, CS, D, DX, DY, F, L, M, R, S, SB, SC, SD, SM, SN, SS, SW, TC, TN, TS, V, W, X, Y, Z, ZR.
5) Extra2 block write option.
0, space : normal Analog write,
1 : output value and address saving for block(multi) write,
2 : sequential block write by using saved data, ( maximum block write count = 256)
3 : random block write by using saved data,
4 : delete all saved data for block write.
Write example 1)
PORT:0, station:255, ADDRESS:0015, Extra1: D, Extra2 : 0
The setting parameter shown above is word write example for D0015 address( word unit ) of D memory.
Write example 2)
PORT:0, station:255, ADDRESS:000A, Extra1: Y, Extra2 : 0
The setting parameter shown above is word write example for Y000A address ( word unit ) of Y memory.
Write example 3)
PORT:0, station:255, ADDRESS:0010, Extra1: DF2, Extra2 : 0
The setting parameter shown above is word write example for D0010+D0011 address ( Float unit ) of D memory.
Write example 4)
PORT:0, station:255, ADDRESS:0010, Extra1: DD2, Extra2 : 0
The setting parameter shown above is word write example for D0010+D0011 address ( Dword unit ) of D memory.
Write example 5)
PORT:0, station:255, ADDRESS:0000, Extra1: W, Extra2 : 1, Output value = 356
The setting parameter shown above is data saving example for block writing. The saved data : Output value = 356, memory type = W, address = 0000.
Also,
PORT:0, station:255, ADDRESS:0001, Extra1: B, Extra2 : 1, Output value = 12
The setting parameter shown above is data saving example for block writing. The saved data : Output value = 12, memory type = B, address = 0001.
Also,
PORT:0, station:255, ADDRESS:0002, Extra1: W, Extra2 : 1, Output value = 34
The setting parameter shown above is data saving example for block writing. The saved data : Output value = 12, memory type = B, address = 0001.
Finally,
PORT:0, station:255, ADDRESS:0005, Extra1: B, Extra2 : 2,
The setting parameter shown above is sequential block write setting example. The writing data are saved data at internal memory, memory type = B, writing address = 5 ~ 7, Output value = 356, 12, 34.
( sequential block write setting use Port, Station, Extra1(memory type) and Address. Output value = don't care )
Write example 6)
PORT:0, station:255, ADDRESS:0005, Extra1: B, Extra2 : 1, Output value = 234
The setting parameter shown above is data saving example for block writing. The saved data : Output value = 234, memory type = B, address = 0005.
Also,
PORT:0, station:255, ADDRESS:0003, Extra1: W, Extra2 : 1, Output value = 45
The setting parameter shown above is data saving example for block writing. The saved data : Output value = 12, memory type = B, address = 0001.
Also,
PORT:0, station:255, ADDRESS:0007, Extra1: B, Extra2 : 1, Output value = 78
The setting parameter shown above is data saving example for block writing. The saved data : Output value = 12, memory type = B, address = 0001.
Finally,
PORT:0, station:255, ADDRESS:0000, Extra1: B, Extra2 : 3,
The setting parameter shown above is random block write setting example.
The writing data are saved data at internal memory,
memory type = B, writing address = 5, Output value = 234,
memory type = W, writing address = 3, Output value = 45,
memory type = B, writing address = 7, Output value = 78.
( random block write setting use Port and Station. Address, Extra1(memory type), Output value = don't care )
Ladder setting for ethernet communication with MELSEC Q Series PLC are as follows :
a) Add 'Ethernet communication module' at Network setting.
b) Input each network number according to PLC status.
b) Select ¡®Ethernet operations¡¯ menu
data code -> binary code,
initial timing -> STOP,
Enable write at RUN time -> check (V).
d) ¡®Open setting¡¯ menu
protocol -> select TCP or UDP,
open system -> Unpassive,
fixed buffer -> send,
fixed buffer communication procedure -> Procedure exist,
pairing open -> disable,
existence confirmation -> don't check,
Host station port no. -> 0500 : hex-decimal number( 0500 = decimal : 1280 ),
Transmission target device IP address -> input IP address of computer (monitoring PC),
Transmission target device port no. -> input equal value with 'local station port number' ( hex-decimal).
e) Download ethernet setting value to PLC.
Please refer to reference manual of Melsec PLC.
<Figure 4> is ethernet operations dialog example of Melsec Q series.
<Figure 5> is network parameter setting example for ethernet communication.
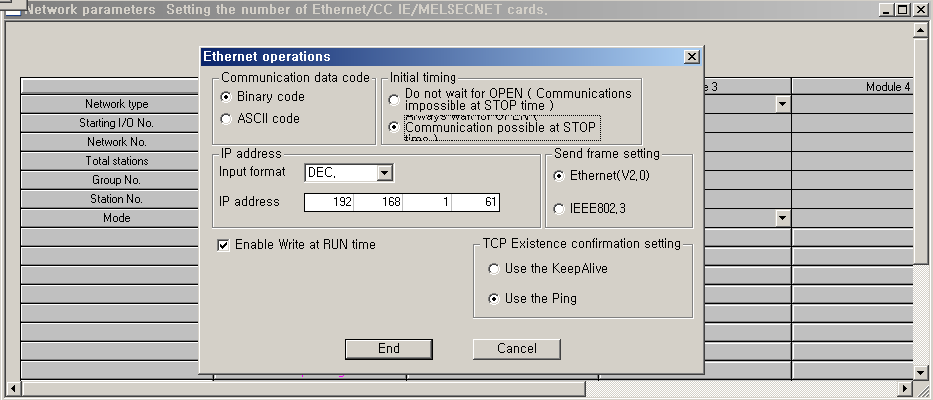 |
| <Figure 4> Ethernet operations dialog example of Melsec Q series |
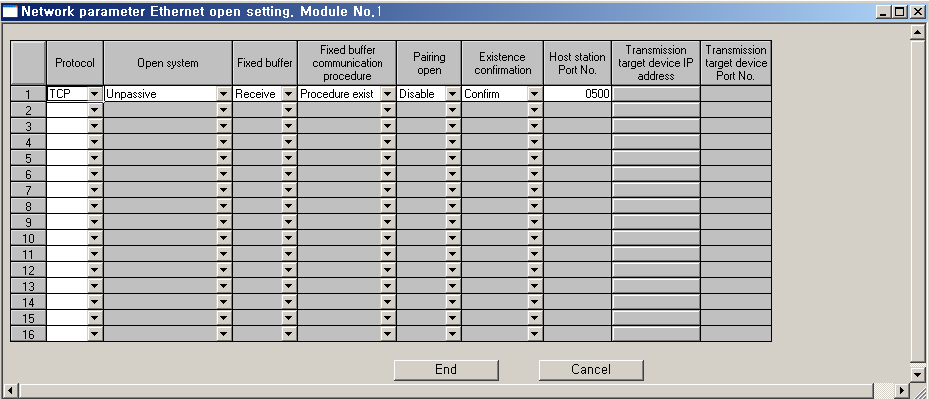 |
| <Figure 5> Network parameter setting example for ethernet communication |