YOKOGAWA FA-M3 Ethernet communication driver is the driver to communicate(ethernet) with PLC of Yokogawa Control Systems Ltd., in Japan.
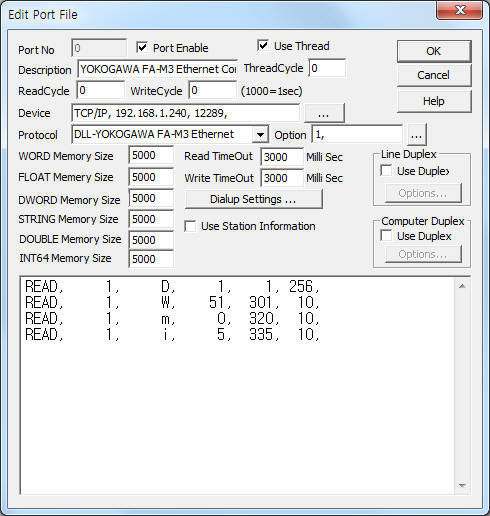
<Figure 1> is read setting example of YOKOGAWA FA-M3 Ethernet communication driver.
 |
| <Figure 1> Read setting example of YOKOGAWA FA-M3 Ethernet communication driver |
Device part of <Figure 1> input Device type(TCP/IP or UDP/IP), IP address of PLC(192.168.1.240 : setting with 8 rotary switch attached at module), service port of TCP/IP(UDP/IP) protocol ( 12289 : fixed ),respectively, according to setting of PLC.
Also you can input 'CPU number of FA-M3 PLC' (1 ~ 4, default = 1) by using option part.
Note) You have to set always 'ON' 1 DIP switch of SW9 at Ehternet communication module, because of YOKOGAWA FA-M3 PLC Ethernet communication driver made by 'Binary DATA CODE'.
<Table 1>, <Table 2> are rotary switch setting method and SW9 DIP switch setting of FA-M3 PLC Ethernet module.
<Figure 2> is appearance of SW1 ~ SW9 setting switch at FA-M3 Ethernet communication module.
SW number |
Contents |
1 |
High Nibble of 1st IP Address |
2 |
Low Nibble of 1st IP Address |
3 |
High Nibble of 2nd IP Address |
4 |
Low Nibble of 2nd IP Address |
5 |
High Nibble of 3rd IP Address |
6 |
Low Nibble of 3rd IP Address |
7 |
High Nibble of 4th IP Address |
8 |
Low Nibble of 4th IP Address |
| <Table 1> Rotary switch setting method of FA-M3 Ethernet module | |
Setting example of IP Address)
If you want 'IP Address = 192.168.1.240' (Dex-decimal : C0.A8.1.F0 )
SW1 = C, SW2 = 0,
SW3 = A, SW4 = 8,
SW5 = 0, SW6 = 1,
SW7 = F, SW8 = 0.
| BIT Position | Contents | OFF | ON |
| 1 | Data Code | ASCII | BINARY (ON for YOKOGAWA FA-M3 Ethernet communication drive) |
| 2 | Protection | NO | YES |
| 3 ~ 6 | Always Off | ||
| 7 | TCP Connection | Close | Hold |
| 8 | Mode | Normal | Test |
| <Table 2> SW9 DIP switch setting of FA-M3 Ethernet module | |||
 |
| <Figure 2> Appearance of SW1 ~ SW9 setting switch at FA-M3 Ethernet communication module |
YOKOGAWA FA-M3 Ethernet communication driver¡¯s read schedule
Read schedule setting parameters are as follows:
1) Station – Don't care.
2) Read Command – Command = B, CI, CP, CS, CU, cu, D, E, e, I, i, L, l, M, m, R, TI, TP, TS, TU, tu, V, W, X, x, Y, y, Z. ( Refer to <Table 4> )
3) Read Start Address – Read start address of each memory.
cu, e, i, l, m, tu, x, y Read command (lowercase letters) : 0 ~, 10 bit unit.
Example1) 0 read start address = 1st Bit ~,
Example2) 1 read start address = 11th Bit ~,
Example3) 2 read start address = 21th Bit ~,
¡¦
Example4) 15 read start address = 151th Bit ~,
¡¦
B, CI, CP, CS, CU, D, E, I, L, M, R, TI, TP, TS, TU, V, W, X, Y, Z Read command : 1 ~ , 1 word unit.
4) Save start address for Communication Server – Saving start address of Communication Server.
5) Read Size – Read size of 10 bit or 1 word unit.
cu, e, i, l, m, tu, x, y Read command : 1 ~ 25 (10 Bit ~ 250 Bit)
B, CI, CP, CS, CU, D, E, I, L, M, R, TI, TP, TS, TU, V, W, X, Y, Z Read command : 1 ~ 256 (1 ~ 256 word)
Read schedule example)
READ, 1, D, 1, 1, 256,
READ, 1, W, 51, 301, 10,
READ, 1, m, 0, 320, 10,
READ, 1, i, 5, 335, 10,
<Table 4> is read command and contents of YOKOGAWA FA-M3 PLC.
Read command (memory type) |
Data type |
Contents |
Read unit |
B |
WORD |
File Register - only F3SP25, F3SP35, F3SP28, F3SP38, F3SP58 CPU module |
WORD unit |
CI |
Counter current value |
||
CP |
Counter Present value |
||
CS |
Counter Setup value |
||
CU |
BIT |
Count-up Relay |
WORD unit |
cu |
10 Bit unit |
||
D |
WORD |
Data Register |
WORD unit |
E |
BIT |
Shared Relay |
WORD unit |
e |
10 Bit unit |
||
I |
Internal Relay |
WORD unit |
|
i |
10 Bit unit |
||
L |
Link Relay |
WORD unit |
|
l |
10 Bit unit |
||
M |
Special Relay |
WORD unit |
|
m |
10 Bit unit |
||
R |
WORD |
Shared Register |
WORD unit |
TI |
Timer current value |
||
TP |
Timer Present value |
||
TS |
Timer Setup value |
||
TU |
BIT |
Time-up Relay |
WORD unit |
tu |
10 Bit unit |
||
V |
WORD |
Index Register |
WORD unit |
W |
Link Register |
||
X |
BIT |
Input Relay |
WORD unit |
x |
10 Bit unit |
||
Y |
Output Relay |
WORD unit |
|
y |
110 Bit unit |
||
Z |
WORD |
Special Register |
WORD unit |
| <Table 4> Read command and contents of YOKOGAWA FA-M3 PLC | |||
Note) cu, e, i, l, m, tu, x, y and CU, E, I, L, M, TU, X, Y read command are equal read of memory area, but read data unit differ 10 bit and word unit.
When you read 10 bit unit, save the readed data form 1 bit(2nd bit) ~ 9 bit(10th bit) of 'Save start address + 0' and 0 bit(1st bit) of of 'Save start address + 1'.
Example) READ, 1, m, 15, 115, 10,
← M (Special Relay) memory area of PLC, address = 151(15 : read start address), read size = 100 bits(10 : read size).
←Save readed data at 1 ~ 9 bit (0 bit = don't save) of 115(115 : Save start address) WORD memory and 0 ~ 9 bit of 116 ~ 124 WORD memory of Communication Server.
←Also, save 0 bit of 125 WORD memory that is last readed data bit.
If you want more information for YOKOGAWA FA-M3 PLC, plsease refer to reference manual of YOKOGAWA FA-M3 PLC.
If you click the icon ![]() in protocol option part, you
can see the dialogue box such as <Figure 3>. you can also set read schedule by
using this part.
in protocol option part, you
can see the dialogue box such as <Figure 3>. you can also set read schedule by
using this part.
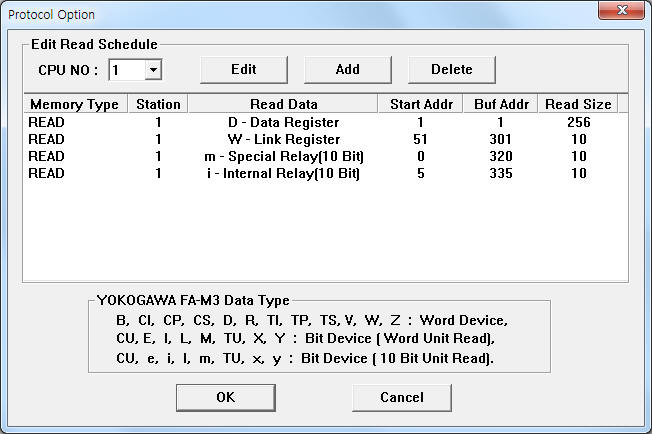 |
| <Figure 3> Example of YOKOGAWA FA-M3 Ethernet communication driver¡¯s Option dialogue box |
You can set read schedule by using ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() button and listbox of <Figure
3>.
button and listbox of <Figure
3>.
CPU number of FA-M3 PLC can input by using the part of ¡®CPU NO¡¯ shown in <Figure 3>.
 |
| <Figure 4> Example of YOKOGAWA FA-M3 Ethernet communication driver¡¯s read schedule Add/Edit dialogue box |
When you click Add button or Edit button in dialogue box of <Figure 3>, dialogue box of <Figure 4> is shown.
You can write the setting value by using write settings.
CS, TS, X memory area are read only memory, so you can't write.
Also at writing settings don't use 'cu, e, i, l, m, tu, y' command.
Digital Write
Digital write setting parameters are as follows:
1) PORT Port no. (0 ~ 255)
2) STATION Don't care.
3) ADDRESS Write address of memory area.
B, CI, CP, D, R, TI, TP, V, W, Z write command : Higher 3 digit = 1 ~ WORD address, Lower 1 digit - 0 ~ F bit position,
(B, CI, CP, D, R, TI, TP, V, W, Z memory area don't support direct bit write, so this driver read 'Word' data and write after bit operation)
CU, E, I, L, M, TU, Y write command : 1 ~ Bit address. (decimal unit : 0001, 0002, ... 0009, 0010, ¡¦)
RESET : Don't care.
4) Extra1 Write command or memory area for writing = B, CI, CP, CU, D, E, I, L, M, R, TI, TP, TU, V, W, Y, Z : memory area for writing, RESET : reset of module write command.
5) Extra2 Don't care.
Write example 1)
PORT:0, Station : 1, Address : 0123, Extra1 : D, EXTRA2 :
The setting parameter shown above is bit control(On/Off) example of 12 Word, 3 Bit(4th) address at 'D' device memory area.
Write example 2)
PORT:0, Station : 1, Address : 012F, Extra1 : D, EXTRA2 :
The setting parameter shown above is bit control(On/Off) example of 12 Word, F Bit(16th) address at 'D' device memory area.
Write example 3)
PORT:0, Station : 1, Address : 0051, Extra1 : M, EXTRA2 :
The setting parameter shown above is bit control(On/Off) example of 51 Bit address at 'M' device memory area.
Write example 4)
PORT:0, Station : 1, Address : 0135, Extra1 : M, EXTRA2 :
The setting parameter shown above is bit control(On/Off) example of 135 Bit address at 'M' device memory area.
Analog Write
Analog write setting parameters are as follows:
1) PORT Port no. (0 ~ 255)
2) STATION Don't care.
3) ADDRESS Write address of memory area.(decimal unit)
B, CI, CP, D, R, TI, TP, V, W, Z write command : 1 ~ WORD address,
CU, E, I, L, M, TU, Y write command : 1 ~ Word address. Write one word(16 bits) data from (Address -1) x 16 + 1 Bit position.
example) Address : 0001 = 1 ~ 16 bit data write , Address : 0002 = 17 ~ 32 Bit data write.
RESET : Don't care.
4) Extra1 Write command or memory area for writing = B, CI, CP, CU, D, E, I, L, M, R, TI, TP, TU, V, W, Y, Z : memory area for writing, RESET : reset of module write command.
5) Extra2 Don't care.
Write example 1)
PORT:0, Station : 1, Address : 0001, Extra1 : D, EXTRA2 :
The setting parameter shown above is word unit write example of 1 Word address at 'D' device memory area.
Write example 2)
PORT:0, Station : 1, Address : 0035, Extra1 : D, EXTRA2 :
The setting parameter shown above is word unit write example of 35 Word address at 'D' device memory area.
Write example 3)
PORT:0, Station : 1, Address : 0001, Extra1 : M, EXTRA2 :
The setting parameter shown above is word unit write example of 1 ~ 16 bits(one word) address at 'M' device memory area.
Write example 4)
PORT:0, Station : 1, Address : 0015, Extra1 : M, EXTRA2 :
The setting parameter shown above is word unit write example of 241 ~ 256 bits(one word) address at 'M' device memory area.
Connection of communication cable and main power are as follows.
Connection of communication cable
Please connect ethernet communication cable of 10 Base T, 10 Base 2, 10 Base 5 to T, AUI, +/- connector such as <Figur 5>.
<Figure 5> is main power and communication cable connection example to FA-M3 PLC.
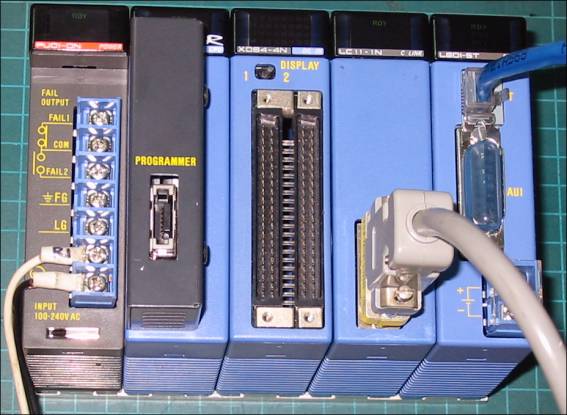 |
| <Figure 5> Main power and communication cable connection example to FA-M3 PLC |
Connection of main power
Please connect 110V AC ( or 100 ~ 240V AC, according to power module) main power to N, L connector to FA-M3 PLC such as <Figure 5>.