CHINO KP1000 Communication Driver is the driver to communicate with PID controller of CHINO Co., Ltd. in Japan.
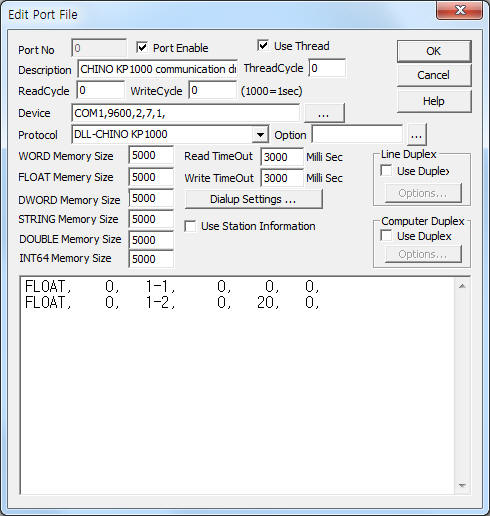
<Figure 1> is read setting example of CHINO KP1000 communication driver.
 |
| <Figure 1> Read setting example of CHINO KP1000 communication driver |
Device part of <Figure 1> input Com Port(COM1), Baud Rate(9600), Parity Bit(2), Data Bit(7), Stop Bit(1) respectively.
CHINO KP1000 controller can set baud rate 300 ~ 9600bps, but parity bit, data bit, stop bit are fixed to 2, 7, 1.
CHINO KP1000 communication driver’s read schedule
Read schedule setting parameters are as follows:
1) STATION – RS-232C : 0, RS-422 : 1~99.
2) Read command – Command( Refer to <Table 1>).
1-1 : Read of Real Data,
1-2 : Read of Execution Parameter,
1-3 : Read of Setting Program Parameter,
1-4 : Read of Individual Setting Parameter,
1-5 : Read of Program Pattern Setting Condition,
1-6 : Read of Unit Status,
1-7 : Read of Mode Lock Status,
1-8 : Read of Status 1,
1-9 : Read of Status 2.
3) Read Start Address – Pattern number of parameter type number, ...
1-3 read command = 0 ~ 19 pattern number.
1-4 read command = 12 ~ 28, 30 ~ 49, 51, 52 Parameter Type number.
Other read command = Don't care.
4) Save start address for Communication Server – Saving start address of Communication Server.
5) Read Size – Step number, parameter number, .... ( Refer to <Table 1> ~ <Table 8> )
1-3 read command = step number,
1-4 read command = parameter number,
Other read command : Fixed to 1.
Read schedule example)
FLOAT, 0, 1-1, 0, 0, 0,
FLOAT, 0, 1-2, 0, 20, 0,
<Table 1> ~ <Table 8> is store values and contents of '1-1', 1-2', 1-3', '1-5', 1-6', 1-8', 1-9' read command.
| Store values | Contents | Remarks |
| Start Addr + 0 | Pattern nunber | 0 ~ 19 |
| Start Addr + 1 | Step number |
|
| Start Addr + 2 | PV status | 0 = Normal 1 = +Over Range 2= -Over Range |
| Start Addr + 3 | PV value |
|
| Start Addr + 4 | SV value |
|
| Start Addr + 5 | Time Display System | 1 = Step Completed 2 = Patterns Completed 3 = Steps Remaining 4 = Patterns Remaining |
| Start Addr + 6 | Time Unit | 1 = minute, 2 = hour, 3 = day |
| Start Addr + 7 | upper time | minute, hour, day |
| Start Addr + 8 | lower time | second, minute, hour |
| Start Addr + 9 | Status 1 | 0 = Auto 1 = Man 2 = AT 3 = PRG. End Out 4 = PV Err Out 5 = FP AT 6 = Reset |
| Start Addr + 10 | MV1 (output value) |
|
| Start Addr + 11 | status 2 | 0 = Auto 1 = Man 2 = AT 3 = PRG. End Out 4 = PV Err Out 5 = FP AT 6 = Reset |
| Start Addr + 12 | MV2 (2nd output value) |
|
| <Table 1> Store values and contents of '1-1' read command | ||
| Store values | Contents | Remarks |
| Start Addr + 0 | Execution Target SV | |
| Start Addr + 1 ~ 3 | Execution P, I, D | |
| Start Addr + 4 ~ 7 | Execution AL1 ~ AL4 | |
| Start Addr + 8 ~ 9 | Execution OL, OH | |
| Start Addr + 10 | Execution change Amount | |
| Start Addr + 11 | Execution Sensor Compensation | |
| Start Addr + 12 ~ 14 | Second P, I, D | |
| <Table 2> Store values and contents of '1-2' read command | ||
| Store values | Contents |
Remarks |
| Start Addr + 0 | Step type |
1 = Step 0 2 = Step N 3 = End Step 6 = Pattern Repeat |
| Start Addr + 1 | Pattern number |
0 ~ 19 |
| Start Addr + 2 | Step number |
|
| Start Addr + 3 | Step 1 = Start SV Step 2 = SV Step 3 = Pattern No. to Link Step 6 = Number of Repeats |
|
| Start Addr + 4 | Step 1 = SV ( 0 ), PV ( 1 ) Start Step 2 = Upper Time Step 3 = End Output |
|
| Start Addr + 5 | When Step 2 = Lower Time |
|
| Start Addr + 6 | When Step 2 = Repeat times |
0 = Repeat Start Step etc = Non-Setting Step |
| Start Addr + 7 | When Step 2 = PID No |
When under Step 2 |
| Start Addr + 8 | ALM No |
|
| Start Addr + 9 | OPL No |
|
| Start Addr + 10 | OSL No |
|
| Start Addr + 11 | Sensor Compensation No |
|
| Start Addr + 12 | Actual Temperature Compensation No |
|
| Start Addr + 13 | Waiting Time No |
|
| Start Addr + 14 ~ 18 | TS1 ~ TS5 |
0 = All OFF 1 = No. 1 2 = No. 1 Repeat … 99 = ALL ON |
| <Table 3> Store values and contents of '1-3' read command | ||
| Store values | Contents | Remarks |
| Start Addr + 0 | Pattern number | 0 ~ 19 |
| Start Addr + 1 | Number of Steps to be Set | 0 = Not Setting |
| <Table 4> Store values and contents of '1-5' read command | ||
Store values |
Contents |
Remarks |
Start Addr + 0 |
1 = Controller 2 = Setter |
|
Start Addr + 1 |
0 = Setter 1 = Thermocouple 2 = Resistance Thermocouple Input |
|
Start Addr + 2 |
First Output |
1 = 61, 65[EMF] 2 = 62 3 = 63[Liner] [ ] is Setter |
Start Addr + 3 |
Second Output |
0 = None 1 = 61, 65 3 = 63 |
Start Addr + 4 |
Transmission |
0 = None 1 = Provider |
Start Addr + 5 |
Time Signal |
|
Start Addr + 6 |
External Drive |
|
Start Addr + 7 |
Pattern Selection |
|
Start Addr + 8 |
Time Unit |
0 = Hours/Minutes 1 = Minutes/Seconds |
| <Table 5> Store values and contents of '1-6' read command | ||
Store values |
Contents |
Remarks |
| Start Addr + 0 | FNC Key |
0 = Not Locked 1 = Locked |
| Start Addr + 1 ~ 9 | Mode 0 ~ Mode 8 |
|
| <Table 6> Store values and contents of '1-7' read command | ||
Store values |
Contents |
Remarks |
| Start Addr + 0 ~ 3 | AL1 ~ AL4 |
00 = Alarm Off 01 = Alarm On 10 = Alarm Off During WAIT |
| Start Addr + 4 | Waiting Time Alarm |
0 = OFF 1 = ON |
| Start Addr + 5 | Error |
0 = Normal 1 = +OR 2 = -OR 4 = Hardware Error |
| Start Addr + 6 ~ 10 | TS1 ~ TS5 Time Signal |
0 = OFF 1 = ON |
| <Table 7> Store values and contents of '1-8' read command | ||
Store values |
Contents |
Remarks |
Start Addr + 0 |
RUN |
1 = RUN |
Start Addr + 1 |
STOP |
1 = STOP |
Start Addr + 2 |
RESET |
1 = RESET |
Start Addr + 3 |
END |
1 = END |
Start Addr + 4 |
ADV |
1 = ADV |
Start Addr + 5 |
CONST |
0 = PRG 1 = CONST |
Start Addr + 6 |
MAN1 |
0 = AUTO 1 = MAN |
Start Addr + 7 |
MAN2 |
|
Start Addr + 8 |
WAIT |
0 = Normal 1 = During Actual Temperature Compensation |
Start Addr + 9 |
AT |
0 = Normal 1 = During AT |
Start Addr + 10 |
FNC Key Lock |
0 = Not Locked 1 = Locked |
Start Addr + 11 |
M/S |
0 = Master 1 = Slave |
| <Table 8> Store values and contents of '1-9' read command | ||
If you click the icon ![]() in
protocol option part, you can see the dialogue box such as <Figure 2>. you can
also set read schedule by using this part.
in
protocol option part, you can see the dialogue box such as <Figure 2>. you can
also set read schedule by using this part.
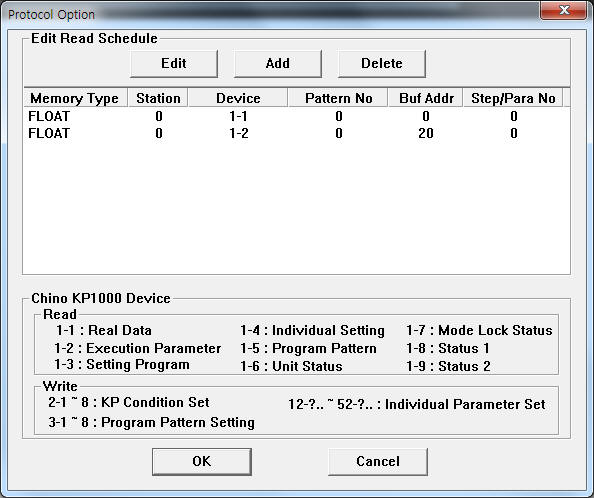 |
| <Figure 2> Example of CHINO KP1000 communication driver’s Option dialogue box |
You can set read schedule by using ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() button and listbox
of <Figure 2>.
button and listbox
of <Figure 2>.
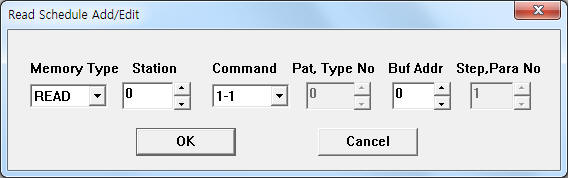 |
| <Figure 3> Example of CHINO KP1000 communication driver’s read schedule Add/Edit dialogue box |
When you click Add button or Edit button in dialogue box of <Figure 2>, dialogue box of <Figure 3> is shown.
You can set CHINO KP1000 controller by using write settings.
Bit Write
Bit write and word write have the same setting parameters except output value.
Word Write
Word write setting parameters are as follows:
1) PORT Port no. (0 ~ 255)
2) STATION RS-232C : 0, RS-422 : 1~99.
3) ADDRESS Writing address, contents, ... ( Refer to <Table 9> ~ <Table 11> ).
4) Extra1 Write command.
2-1 ~ 2-8 : KP status output, ( Refer to <Table 9> )
3-1 ~ 3-8 : Program Pattern Setting, ( Refer to <Table 10> )
12-? ~ 52-? : Individual Parameter Setting. ( Refer to <Table 11> )
5) Extra2 Output status, contents.... ( Refer to <Table 9> ~ <Table 11> ).
| Extra1 (Write command) |
Address | Extra2 | Output value | Output condition | Output contents |
| 2-1 | Don't care | Pattern number | 1 = Run 2 = Stop 3 = ADV 4 = Reset 5 = Pattern Select |
FNC = Lock | Program Drive |
| 2-2 | Output type - 0 = P 1 = I 2 = D 3 ~ 6 = AL1 ~ 4 7 = OL 8 = OH 9 = OSL 10=Sensor Comp. |
Don't care | Output value according to address | Mode 0 =
Lock' Reading after write form '1-2' read command expect 'Output contents' |
Execution Parameter Setting |
| 2-3 | Output type- 0= MV1 Auto/Man 1= MV1 Setting value 2= MV2 Auto/Man 3= MV2 Setting value |
0=Saving to internal memory 1=Output data from saved memory |
Output value according to address Auto/Man ( 0, 2) = 0 (AUTO), 1 (MAN) |
FNC = Lock | Auto/Man Switching |
| 2-4 | Don't care | 0 = PRG 1 = CONST |
SV setting value | Mode 1 = Lock | Constant Value Control |
| 2-5 | Don't care | Don't care | Don't care | Alarm Reset | |
| 2-6 | Don't care | Don't care | 0 = AT Stop 1 ~ 3 = AT1 ~ AT3 Start |
Auto Tuning Start/Stop | |
| 2-7 | Output type- 0 = FNC Lock 1 ~ 9 = Mode0 ~ 8 |
Don't care | 0 = Not Locked 1 = Locked |
Reading after write form '1-7' read command expect 'Output contents' | Mode Lock/Unlock |
| 2-8 | Don't care | Don't care | 1 = Steps Completed 2 = Patterns Completed 3 = Steps Remaining 4 = Patterns Remaining |
Mode 1 = Lock | Time Display System |
| <Table 9> Output parameter value and contents of 2-1 ~ 2-8 (KP status) write command | |||||
| Extra1 (Write command) |
Address | Extra2 | Output value | Output condition | Output contents |
3-1-? (? = 0~19 Pattern No) |
Don't care | 0 = SV Start 1 = PV Start |
Start SV setting value | only RESET
Mode 2 = Lock |
Step 0 |
3-2-?-n (? = 0~19 Pattern No, n = Step No) |
Don't care | Setting time higher 2_3 digit: upper time lower 2 digit: lower time) |
SV output value | Step n | |
3-3-?-n (? = 0~19 Pattern No, n = Step No) |
Don't care | Pattern No. to Link
0 = No Link |
Output in End
0 = Output 0 200 = Constant Value Control |
End Step | |
3-4-?-n (? = 0~19 Pattern No, n = Step No) |
0= PID No. 1= ALM No. 2= OPL No. 3= OSL No. 4= Sensor No. 5= Act Temp 6= Wait Time 7~11= TS1~5 |
0=Saving to internal memory
1 = Output data from saved memory |
Output value according to address
Refer to <Table 3> of Step 2 |
Parameter No. Setting |
|
3-5-? (? = 0~19 Pattern No.) |
Starting Step No. | End Step No.
( Start < End ) |
Number of times
00 = To Release Repeat |
Step Repeat | |
3-6 |
Don't care | Don't care | Number of Repeats | Pattern Repeat |
|
3-7-? (? = 0~19 Pattern No.) to be copied Pattern number |
Don't care | Don't care | Pattern No. to Hold Copied Pattern |
Pattern Copy | |
3-8 |
Don't care | Don't care | Cleared Pattern number 0 = All Clear 1 ~ 19 = To be Clear number. |
Pattern Clear | |
| <Table 10> Output parameter value and contents of 3-1 ~ 3-8 (Program Pattern Setting) write command | |||||
| Extra1 (Write command) |
Address | Extra2 | Output value | Output condition | Output contents |
12-0 |
0 = AL1 1 = AL2 2 = AL3 3 = AL4 |
0=Saving to internal memory
1 = Output data from saved memory |
Address에 따른 AL1 ~ AL4설정 값 |
Mode 3 = Lock | 1 ~ 8 All Alarm value Setting |
12-? ( ? = 1 ~ 8 Alarm No. ) |
0 = AL1 1 = AL2 2 = AL3 3 = AL4 |
Don't care | Setting value of Alarm ( AL1 ~ AL3) |
Mode 3 = Lock
Write after readed 1-4 read command |
Setting of Alarm value |
13-? ( ? = 0 ~ 8, 90 ~ 98 PID No. ) |
Setting value of P | Setting value of I | Setting value of D | Mode 3 = Lock | Setting value of PID 0 PID = 1 ~ 8 All parameter setting, 90 PID = 91 ~ 98 All parameter setting |
14-? ( ? = 0 ~ 8 Para. No. ) |
Don't care | Don't care | Output Change Limit |
Mode 4 = Lock | Output Change Limit 0 = 1 ~ 8 All parameter setting |
15-? ( ? = 0 ~ 8 Para. No. ) |
Don't care | Setting value of OL-L | Setting value of OL-H |
Output High/Low Limit 0 = 1 ~ 8 All parameter setting |
|
16-? ( ? = 0 ~ 8 Para. No. ) |
Don't care | Don't care | Setting value of Sensor Compensation |
Mode 5 = Lock | Sensor Compensation 0 = 1 ~ 8 All parameter setting |
17-? ( ? = 0 ~ 8 Para. No. ) |
Don't care | Don't care | Setting value of Actual Temperature Compensation |
Mode 6 = Lock | Actual Temp. Compensation 0 = 1 ~ 8 All parameter setting |
18-? ( ? = 0 ~ 8 Para. No. ) |
Don't care | Don't care | Setting value of Waiting Time Alarm |
Waiting Time Alarm 0 = 1 ~ 8 All parameter setting |
|
19-? ( ? = 0 ~ 8 Para. No. ) |
Don't care | Setting value of On Time |
Setting value of Off Time |
Time Signal 0 = 1 ~ 8 All parameter setting |
|
20 |
Don't care | Don't care | Setting value of Digital Filter | Mode 5 = Lock | Digital Filter |
21 |
Trans Type ( 0 = SV, 1 = PV, 2 = MV1, 4 = MV2) |
Scale Min | Scale Max | Mode 7 = Lock | Trans Type/Scale |
| 22 | Don't care | Don't care | Second Output Gap value | Mode 3 = Lock | Second Output Gap |
| 23 | Second P | Second I | Second D | Second Output PID | |
| 24 | Don't care | Don't care | Setting value of Second Output Change Limit |
Mode 4 = Lock | Second Output Change Limit |
| 25 | Don't care | Second OL | Second OH | Second Output high/low Limit | |
| 26 | Don't care | Don't care | Setting value of Second On/Off Deadband |
Mode 3 = Lock | Second On/Off Deadband |
| 27 | Don't care | Don't care | Setting value of Second PV Abnormal Output |
Mode 4 = Lock | Second PV Abnormal Output |
| 28 | Don't care | Don't care | 0 = Direct 1 = Reverse |
Second Output Direct/Rev. | |
| 30 | Input Type value | Don't care | 0 = ℃ 1 = ℉ 2 = K 3 = ℅ 4 = BLK |
Mode 5 = Lock | Measurement Input Unit |
| 31 | Don't care | Don't care | 0 = INT 1 = EXT |
CJ INT/EXT | |
| 32 | Don't care | Don't care | Number of SV Decimal Point | SV Decimal Point | |
| 33 | Don't care | Don't care | Number of PV Decimal Point | PV Decimal Point | |
| 34 | Don't care | Don't care | Setting value of Alarm Filter | Mode 3 = Lock | Alarm Filter |
35-? ( ? = 0 ~ 4 Para. No. ) |
Don't care | Alarm Mode (0 = KH, 1 = DHW, 2 = DL, 3 = DLW, 4 = AH, 5 = AL) |
Setting value of Deadband | Alarm Mode/Deadband 0 = 1 ~ 4 All parameter setting |
|
| 36 | Don't care | Don't care | Deadband On/Off | Deadband On/Off | |
| 37 | Don't care | Don't care | Pluse Cycle | Mode 4 = Lock | Pluse Cycle |
| 38 | Setting value of Zero | Setting value of Span | Setting value of Gain | FB Zero/Span/Gain | |
| 39 | Don't care | Don't care | Setting value of Preset | Output Preset | |
| 40 | Don't care | Don't care | Setting value of PV Abnormal Output |
PV Abnormal Output | |
| 41 | Don't care | Don't care | 0 = Direct 1 = Reverse |
Output Direct/Reverse | |
| 42 | Don't care | Setting value of Zero | Setting value of Span | Mode 5 = Lock | Linear Range |
| 43 | Don't care | Setting value of Min | Setting value of Max | Linear Scale | |
| 44 | Don't care | Setting value of Low Limit | Setting value of High Limit | Mode 3 = Lock | ARW |
45-? ( ? = 0 ~ 8 Para. No. ) |
Don't care | 0 = Off 1 = On |
Setting value of AT2 SV | AT2 SV 0 = 1 ~ 8 All parameter setting |
|
46-? ( ? = 1 ~ 7 Para. No. ) |
Don't care | Don't care | Setting value of SV Range | SV Range (AT3) | |
47-? ( ? = 1 ~ 8 Para. No. ) |
Don't care | 0 = Off 1 = On |
Setting value of AT3 SV | AT3 SV | |
| 48 | Don't care | Don't care | 0 = Up 1 = Down |
AT Start Direction | |
| 49 | Don't care | Don't care | Setting value of SV in Reset | Mode 2 = Lock | SV in Reset |
| 51 | Thermocouple Type No. |
Don't care | 0 = ℃ 1 = ℉ 2 = K 3 = ℅ 4 = BLK |
Mode 5 = Lock | Thermocouple Type/Unit |
| 52 | Don't care |
Setting value of Min | Setting value of Max | SV Scale | |
| <Table 10> Output parameter value and contents of 12 ~ 52 (Individual Parameter Setting) write command | |||||
Write example 1)
PORT : 0 STATION : 0 ADDRESS : 0000 EXTRA1 : 2-1 EXTRA2 : 1
The setting parameter shown above is an example of write for program drive state(output value : 1 = Run, 2 = Stop, 3 = ADV, 4 = Reset, 5 = Pattern Select) of pattern 1.
Write example 2)
PORT : 0 STATION : 0 ADDRESS : 0000 EXTRA1 : 2-2 EXTRA2 :
The setting parameter shown above is an example of write for 'P' value of execution parameter.
Write example 3)
PORT : 0 STATION : 0 ADDRESS : 0002 EXTRA1 : 2-2 EXTRA2 :
The setting parameter shown above is an example of write for 'D' value of execution parameter.
Write example 4)
PORT : 0 STATION : 0 ADDRESS : 0001 EXTRA1 : 2-3 EXTRA2 : 0
The setting parameter shown above is an example of write for 'MV1' value of Auto/Manual switching. ( When Extra2 = 0, saving to internal memory )
Write example 5)
PORT : 0 STATION : 0 ADDRESS : 0003 EXTRA1 : 2-3 EXTRA2 : 1
The setting parameter shown above is an example of write for 'MV2' value of Auto/Manual switching.(When Extar2 = 1, output data from saved memory )
Write example 6)
PORT : 0 STATION : 0 ADDRESS : 0003 EXTRA1 : 3-2-1-1 EXTRA2 : 200
The setting parameter shown above is an example of write for 'SV' value and setting time(time = 200) of pattern 1.
Write example 7)
PORT : 0 STATION : 0 ADDRESS : 0003 EXTRA1 : 3-6 EXTRA2 :
The setting parameter shown above is an example of write for 'Pattern Repeat ' value.
Write example 8)
PORT : 0 STATION : 0 ADDRESS : 0003 EXTRA1 : 12-1 EXTRA2 :
The setting parameter shown above is an example of write for 'AL3' value.
( AL1 ~ AL3 value set from readed data by1-4 read command )
Write example 9)
PORT : 0 STATION : 0 ADDRESS : 0120 EXTRA1 : 13-8 EXTRA2 : 55
The setting parameter shown above is an example of write for 'P'( 120 ), 'I'( 55 ), 'D'( output value ) value of number 8 PID.
Write example 10)
PORT : 0 STATION : 0 ADDRESS : 0020 EXTRA1 : 23 EXTRA2 : 30
The setting parameter shown above is an example of write for 'Second P'( 20 ), 'Second I'( 30 ), 'Second D'( output value ) value.
Write example 11)
PORT : 0 STATION : 0 ADDRESS : 0080 EXTRA1 : 38 EXTRA2 : 70
The setting parameter shown above is an example of write for 'Zero'( 80 ), 'Span'( 70 ), 'Gain'( output value ) value.
Write example 12)
PORT : 0 STATION : 0 ADDRESS : 0000 EXTRA1 : 33 EXTRA2 :
The setting parameter shown above is an example of write for 'PV Decimal Point'( output value ) value.
Write example 13)
PORT : 0 STATION : 0 ADDRESS : 0000 EXTRA1 : 41 EXTRA2 :
The setting parameter shown above is an example of write for Output Reverse(output value = 1) or Output Direct (output value = 0).
Write example 14)
PORT : 0 STATION : 0 ADDRESS : 0000 EXTRA1 : 43 EXTRA2 : 50
The setting parameter shown above is an example of write for 'Min of Liner Scale '( 50 ), 'Max of Liner Scale '( output value ) value.
Write example 15)
PORT : 0 STATION : 0 ADDRESS : 0000 EXTRA1 : 52 EXTRA2 : 30
The setting parameter shown above is an example of write for 'Min of SV Scale'( 30 ), 'Max of SV Scale '( output value ) value.
Connection of main power line and communication cable are as follows.
Connection of communication cable
CHINO KP1000 controller can communicate RS-232C and RS-422 mode.
<Figure 4> is wiring of RS-232C cable and <Figure 5>is wiring of RS-422 cable.
KP1000 side computer side ( 9 pin connector )
connector 11 (Rx : RD) ------------------------- Tx : SD ( 3 )
connector 12 (Tx : SD) ------------------------- Rx : RD ( 2 )
connector 13 (Ground) ------------------------- Ground( 5 )
<Figure 4> wiring of RS-232C cable
KP1000 side RS-422 connector of computer side
connector 11 (RDA) ------------------------- SDA(T+)
connector 12 (RDB) ------------------------- SDB(T-)
connector 13 (SDA) ------------------------- RDA(R+)
connector 14 (SDB) ------------------------- RDB(R-)
<Figure 5> wiring of RS-422 cable
<Figure 6> is a connection example of main power line and RS-232C communication cable to KP1000 controller.
<Figure 7> shows the appearance of KP1000 controller.
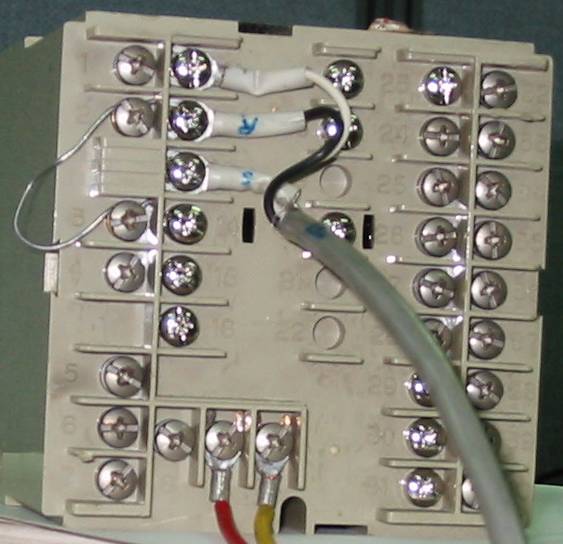 |
| <Figure 6> Connection example of main power line and RS-232C communication cable to KP1000 controller |
Connection of main power line
Please connect main power line to connector 9, 10, AC 85 ~ 264V 50/60 HZ such as <Figure 6>.
 |
| <Figure 7> Appearance of KP1000 controller |