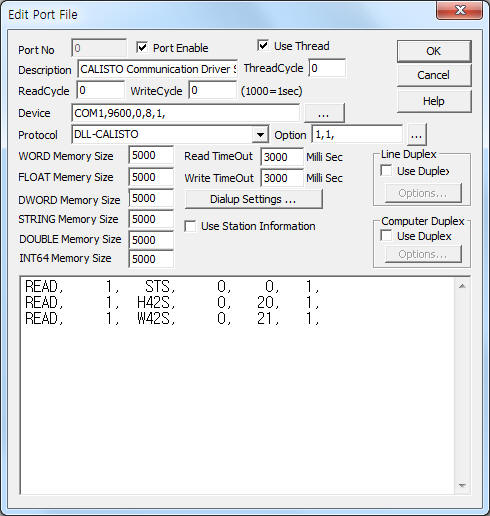
CALISTO Communication Driver is the driver to communicate with dissolved hydrogen and dissolved water controller of MORGAN SCHAFFER SYSTEMS in Canada.
<Figure 1> is read setting example of CALISTO communication driver.
 |
| <Figure 1> Read setting example of CALISTO communication driver |
Device part of <Figure 1> input Com Port(COM1), Baud Rate(9600), Parity Bit(0), Data Bit(8), Stop Bit(1) respectively.
Also whether to use the 'Addressing mode'(0: don't use : terminal mode, 1 : use, default = 1) and to save MDB after reading 'Bank String' data (0: don't save, 1 : save, default = 1) are set by using option part.
Option part of each argument is a comma-delimited.
CALISTO communication driver’s read schedule
Read schedule setting parameters are as follows:
1) STATION – Station number = 0 ~ 99. When ternimal mode station number = don't care.
2) Read command – Read command = STS, OWNR, TRLO, TRID, ID485, DPCD, PHON, AALT, WAMO, ALMO, HA1S, HA2S, WA1S, WA2S, CHAL, CWAL, H42S, W42S, DATE, TIME, WSMO, WPPM. (Refer to <Table 1> )
3) Read start address –Don't care.
4) Save start address for Communication Server – Saving start address of Communication Server.
5) Read Size – Size = Fix to 1. ( Refer to <Table 1> )
Read schedule example)
READ, 1, STS,
0, 0, 1,
READ,
1, H42S, 0, 20,
1,
READ, 1, W42S,
0, 21, 1,
<Table 1> is a description of normal read/write command types and contents of CALISTO communication driver.
<Table 2> is Bank String ( Internally Saved Data ) read/write command types and contents.
<Table 3> is a description of store values and contents of STS read command, <Table 4> is store values and contents of Bank String( Bottom, Top, Next, Prev ) read command.
| Command | Contents |
Read/Write |
Remarks |
| STS | Read of Status String |
Read only |
Refer to <Table 3> |
| OWNR | Owner of Unit or Transformer |
Read/Write |
Max 20 character(alphabet) |
| TRLO | Transformer Location |
||
| TRID | Transformer Identification |
||
| ID485 | Identification RS-485 |
0 ~ 99 |
|
| DPCD | Dump Customer Data |
Read only |
|
| PHON | Emergency Phone Number |
Read/Write |
Max 20 character(alphabet) |
| AALT | All Alarm Type |
Normal = 0, Inverse = 1 |
|
| WAMO | Water Alarm Mode |
Single = 0, Dual = 1 |
|
| ALMO | All Alarm Mode |
Disabled = 0, Full = 1, Simple = 2, Test = 3 |
|
| HA1S, HA2S | Hydrogen Alarm 1/2 Set Point |
-50000 ~ 50000 PPM |
|
| WA1S, WA2S | Water Alarm 1/2 Set Point |
-500 ~ 500 PPM or % |
|
| CHAL, CWAL | Clear Hydrogen/Water Alarm |
0 ~ 99.00 Minutes |
|
| H42S | Hydrogen 4-20 Scale |
100 ~ 50000 PPM |
|
| W42S | Water 4-20 Scale |
10 ~ 500 % or PPM |
|
| DATE | Read/Write of controller's date |
YYYY/MM/DD |
|
| TIME | Read/Write of controller's time |
HH:MM:SS |
|
| WSMO | Water Sensor Mode |
Saturation = 0, PPM = 1 |
|
| WPPM | Water PPM Conversion Factor |
0.05 ~ 3.00 PPM or %RS |
|
| <Table 1> Normal read/write command types and contents of CALISTO communication driver | |||
| Command | Contents |
| BOTTOM | Read of one latest saved data |
| TOP | Read of one first saved data |
| The Unit Sends the Record Located at the Point Location at the Time of the Request | |
| NEXT 1 ~ 10 | Read of 1 ~ 10 next data from current position |
| PREV 1 ~ 10 | Read of 1 ~ 10 previous data from current position |
| DBSIZE | Read of total data size |
| LOCKDB ENABLED/DISABLED | 저장된 Bank String 데이터의 LOCK Enable/Disable |
| <Table 2> Bank String ( Internally Saved Data ) read/write command types and contents of CALISTO communication driver | |
Store Values |
Contents |
Start Addr + 0 ~ 2 |
current year, month, day |
Start Addr + 3 ~ 5 |
current hour, minute, second |
Start Addr + 6 |
Unit Serial Number ( character : always 0 ) |
Start Addr + 7 |
Last Saved Hydrogen |
Start Addr + 8 |
Continuous Hydrogen |
Start Addr + 9 |
Water Content Mode number 0 = Water Content in PPM, 1 = Relative Saturation at 25 °C, 2 = Calculated Water in Transformer |
Start Addr + 10 |
Oil temp in Transformer ( 1 decimal point ) |
Start Addr + 11 ~ 12 |
Hydrogen Alarm 1/2 ( 1 = ON, 0 = OFF ) |
Start Addr + 13 ~ 14 |
Water Alarm 1/2 ( 1 = ON, 0 = OFF ) |
Start Addr + 15 |
Error Code |
| <Table 3> Store values and contents of STS read command | |
Store Values |
Contents |
Remarks |
Start Addr + 0 ~ 2 |
current year, month, day |
|
Start Addr + 3 ~ 5 |
current hour, minute, second |
|
Start Addr + 4 |
Hydrogen Content |
PPM : 5 digit number |
Start Addr + 5 |
Water PPM |
PPM : 5 digit number |
Start Addr + 6 |
Water RS |
%RS : 3 digit number |
Start Addr + 7 |
Water Transformer |
|
Start Addr + 8 |
Cell Temp |
oC : +/- 2 decimal point |
Start Addr + 9 |
Box Temp |
oC : +/- 1 decimal point |
Start Addr + 10 |
Oil Temp |
|
Start Addr + 11 |
Heat Sink Temp |
|
Start Addr + 12 |
Transformer Oil Temp |
|
Start Addr + 13 |
Response Factor |
PPM/mV : 2 decimal point |
Start Addr + 14 |
Volt Zero |
mV : +/- 3 decimal point |
Start Addr + 15 |
Volt Mixing |
|
Start Addr + 16 |
Volt Removing |
|
Start Addr + 17 |
Last Zero |
|
Start Addr + 18 |
High Hydrogen Offset |
PPM : +/- 4 digit number |
Start Addr + 19 |
Cell Offset |
|
| <Table 4> store values and contents of Bank String( Bottom, Top, Next, Prev ) read command. | ||
Note) To save MDB after reading 'Bank String' data (0: don't save, 1 : save, default = 1) are set by using option part.
When saving to MDB, the saving filename is 'Data folder\CALISTO\CALISTO_%05d'. ( %05d = read start address(Read) or Extra2 value(Write) )
CALISTO communication driver store the same data in WORD, DWORD, FLOAT, STRING memory, but the data format are different.
If you click the icon ![]() in protocol option
part, you can see the dialogue box such as <Figure 2>. you can also set read
schedule by using this part.
in protocol option
part, you can see the dialogue box such as <Figure 2>. you can also set read
schedule by using this part.
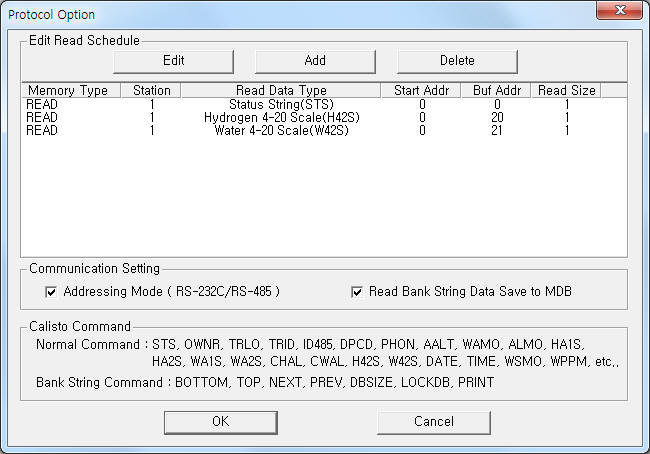 |
| <Figure 2> Example of CALISTO communication driver’s Option dialogue box |
Whether to use the 'Addressing mode' and to save MDB after reading 'Bank String' data are set by using the part of ‘Addressing Mode (RS-232C/RS-485)’, ‘Read Bank String Data Save to MDB’ shown in <Figure 2>
You can set read schedule by using ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() button and listbox
of <Figure 2>.
button and listbox
of <Figure 2>.
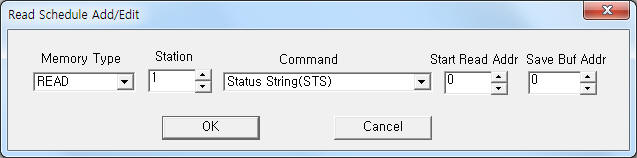 |
| <Figure 3> Example of CALISTO communication driver’s read schedule Add/Edit dialogue box |
When you click Add button or Edit button in dialogue box of <Figure 2>, dialogue box of <Figure 3> is shown.
You can read and write of CALISTO equipment by using write settings.
Bit Write
Bit write setting parameters are as follows:
1) PORT port no. (0 ~ 255)
2) STATION station number = 0 ~ 99. When ternimal mode station number = don't care.
3) ADDRESS saving start address when read command(10 digit number).
4) Extra1 read/write command = STS, OWNR, TRLO, TRID, ID485, DPCD, PHON, AALT, WAMO, ALMO, HA1S, HA2S, WA1S, WA2S, CHAL, CWAL, H42S, W42S, DATE, TIME, WSMO, WPPM. (refer to <Table 1>)
5) Extra2 read, write or Bans String MDB filename nunber.
1 : write, 0 : read, when Bank String data reading : saving MDB filename number( CALISTO_00000.MDB ~ CALISTO_65535.MDB).
Note) 'OWNR, TRLO, TRID, ID485, PHON' write command are set 'Extra2 : 0', 'Extra1' equal as follows.
example 1) Extra1 : OWNR USER1
example 2) Extra1 : TRLO COMPANY01
Write example 1)
Station : 1 Address : 0050 Extra1 : STS, EXTRA2 : 0
The setting parameter shown above is an example of bit write for reading 'status string' and save the readed data from 50 memory address(WORD, DWORD, FLOAT, STRING).
Write example 2)
Station : 1 Address : 0100 Extra1 : AALT, EXTRA2 : 1
The setting parameter shown above is an example of bit write for 'All Alarm Type'(Normal = OFF , Inverse = ON ) and save status the value from 100 memory address(WORD, DWORD, FLOAT, STRING).
Word Write
Word write and bit write have the same setting parameters except output value.
Write example 1)
Station : 1 Address : 0120 Extra1 : H42S, EXTRA2 : 1
The setting parameter shown above is an example of word write for 'Hydrogen 4-20 Scale' and save the setting value at 120 memory address(WORD, DWORD, FLOAT, STRING).
Write example 2)
Station : 1 Address : 0130 Extra1 : W42S, EXTRA2 : 1
The setting parameter shown above is an example of word write for 'Water 4-20 Scale' and save the setting value at 120 memory address(WORD, DWORD, FLOAT, STRING).
Connection of main power line and communication cable are as follows.
Connection of main power line
Please connect main power input AC 200V... to 2, 3 connector such as <Figure 4>.
<Figure 5> is appearance of CALISTO equipment.
 |
| <Figure 4> Connection example of main power line and communication cable |
Communication cable's connection of terminal mode
When you using terminal mode, connect terminal mode dedicated cable. Terminal mode dedicated cable is provided when you purchased.
 |
| <Figure 5> Appearance of CALISTO equipment |
Connection of RS-232C communication cable
RS-232C cable connect 15( Ground ), 16( Rx ), 17( Rx ) of calisto's connector and Ground, Tx, Rx computer's connector.
Computer's 9pin connector CALISTO's connector
Rx ( 2 ) --------------------------------- Tx ( 17 )
Tx ( 3 ) --------------------------------- Rx ( 16 )
G (5 ) --------------------------------- Ground ( 15 )
Connection of RS-485 communication cable
RS-485 cable connect A( + ), B( - ) of calisto's connector and TX+ RX+, Tx-, Rx- computer's connector.
Computer's 9pin connector CALISTO's connector
Tx+, Rx+ --------------------------------- A ( 14 )
Tx-, Rx- ---------------------------------- B ( 13 )
Ground --------------------------------- Ground ( 12 )
Note) When you setting baud rate, address of calisto equipment, ... please use terminal mode communication. ( terminal mode's baud rate = fixed to 9600, 0, 8, 1 )